Abstracts of Teaching
Development and Language Enhancement Grant for 2022-25 Triennium
|
No. |
Project Title |
Abstract |
|
1. |
Review on the 2019 – 22 TDLEG projects –
Identifying and Promoting Good Practices and Pedagogies |
· Over the years, CUHK teachers have been
supported by the TDLEG schemes to formulate new and innovative pedagogies and
curriculum design. Many TDLEG projects
have demonstrated success in diversifying learning activities, revitalizing
students’ learning experiences, and enhancing the teaching quality as a
result. Dissemination and diffusion of
these outstanding practices to CUHK teachers is beneficial to the University
in terms of enhancement of educational provision. · Supported by a TDLEG, CLEAR has been
sustaining and disseminating exemplary TDLEG projects. We reviewed all funded
projects and selected those which created impact on student learning. The
principal supervisors of selected projects were interviewed regarding the
outcomes, sustainability and transferability of the projects. Their advice and recommendations, together
with details about the projects, were included in the online modules housed
in a designated website. · The current proposal is a continuing
project. We plan to review the 200+ projects funded by the 2019-2022 TDLEG
and select those projects considered exemplary and worth diffusion. Based on
the experience gained in reviewing the 2016 – 19 TDLEG projects, it is
estimated that around 40 projects will be identified as exemplary. The principal supervisors of these projects
will be approached for more project details and examples of good practice.
For each selected project, an online module which outlines the project
details focusing on the innovative elements of the pedagogies, curriculum
design, learning activities and deliverables and their positive impacts will
be developed. These modules will be promoted to CUHK teachers via the
designated website and sharing sessions. It is intended that this one-stop
consolidated package of outstanding projects will bring insights to teachers
who may be inspired to adopt similar practices in their own curriculum or
collaborate with teachers in other disciplines thus leading to enhancement in
teaching quality. |
|
2. |
Supporting Academic Quality Assurance –
Further Enhancement of the Database Management System (uPRDatabase)
for Undergraduate Programme Reviews |
·
Programme review is one of the internal quality assurance
strategies in the university. A basket of useful information about
university’s educational outcomes and programme management as retrieved from
the programme reviews and their reports could be capitalised on for further enhancement of the internal quality assurance
strategy of the university. ·
To enhance the storage, retrieval and usage of the valuable data
collected from the various cycles of programme review, uPRDatabase, the first version of a database management system for the
undergraduate programme review reports, was developed with the support from
the 19 - 22 TDLEG. This database platform, equipped with digitalised
information, provides the university stakeholders a holistic picture of
programme performance across different cycles of programme reviews. · This proposed project continuing from the
TDLEG (2019-22) entitled ‘Developing the
database management system (uPRDatabase)
for the undergraduate programme review reports to support academic quality
assurance’ is designed to enhance the
functionalities and sustain uPRDatabase. Many new features and functionalities
are proposed and among them are usage analytics, visualisation
of data analysis and the implementation of the DUO Two Factor
Authentication (2FA) for security purposes. |
|
3. |
Promoting and Sustaining Good Practices and
Pedagogies from Two Cycles of Undergraduate Programme Reviews |
· This project is a continuing project from the TDLEG (2019-22) project
entitled ‘Promoting good practices and pedagogies from the third-cycle
undergraduate programme reviews’. Both projects share the same objectives, which
are, to identify and to disseminate good practices in teaching and learning
and programme management. · One deliverable of the 2019 – 22 project is a report on a comprehensive
analysis on the programme performance between the 2nd and 3rd
cycle reviews. This trend analysis has generated a list of sustaining good
practices in teaching and programme management. The current proposal is
designed to develop video-clips focusing on how such good practices could be
sustained over a span of 10 years (2 programme review cycles). · The 2019 -22 project identified nine programmes
with outstanding performance in the third programme review. From all these
nine programmes, a total of 91 good practices in a
range of review areas was identified and could be disseminated via video
clips. These clips were developed after collecting additional information
from directors of respective programmes. · Due to resources available, the adverse impact of the COVID on work
arrangements and the unexpected substantial number of good practices
identified, work on a few programmes and their
respective good practices could be furthered. The current proposed project
will continue to develop dissemination video clips on a wider range of good
practices. · The website which was developed to house these clips will be reviewed
and updated to enhance sustainability (for future rounds of programme
reviews) and accessibility. · A session to launch the project website will be organised
before the next programme review cycle. |
|
4. |
Resources for Teachers on Rapport Building
with and among Students |
Student connectedness
with teachers and peer has been linked to academic success and social
development. A good teacher-student
relationship (TSR) is found to have positive impacts on students’ academic
performance, affect, behavior and motivation in class (Brinkworth, Mcintyre,
and Gehlbach, 2018). Reciprocally, a well-formed
TSR would also impact on teachers’ positive emotions (Hagenauer
and Someone, 2014) and better approaches to teaching (Wilcon, 1992). Studies also reveal that good
student-student relationship (SSR) is effective in reducing students’
negative perceptions of workload (Kember, 2004) and
in enhancing peer learning (Boud, Cohen, and Sampson, 2013). In the context of CUHK, findings from the Student Experience
Questionnaire (SEQ), which gauges second- and final-year students’ perception
of their capability development and teaching and learning environment,
indicate that among the 9 scales under teaching and learning, ‘student
teacher relationships’ has consistently been ranked the highest whereas
‘relationship with other students’ is among the lowest scales for many years.
Against this background, this proposed project is
designed to sustain the culture of
close TSR and to promote a positive SSR at CUHK by (1) exploring in depth the
SEQ findings regarding TSR and SSR and (2) developing resources for teachers
on principles and strategies to foster rapport building with students and among
students. |
|
5. |
Resources for Teachers on Promoting Active
Learning and Student Engagement |
· Student engagement in active learning has
been established as one of the critical factors which determine academic
success (Parkin, 2017). Promoting student engagement in face-to-face teaching
is always challenging and such challenges are intensified when teaching
online. Undoubtedly, teachers, both new and experienced, are confronted by
the need to be equipped with strategies to enhance student engagement in
different modes of learning (e.g., on-site, online, independent, workplace). · Against this background, the project is
designed to support teachers by developing online resources on promoting
student engagement and active learning. These resources will focus on
approaches and strategies for fostering student engagement and active learning.
These strategies span from course design, design and conduct of learning
activities, assessment task design, classroom interaction techniques, use of
technology, supervision techniques, etc.
· A student survey and teacher interviews
will be conducted to ascertain the current situation in terms of student
engagement and active learning in addition to literature review on current
good practices. Online modules will be developed to demonstrate good
practices. · An additional feature of this project is
that some strategies proposed in these modules will be field-tested by having
project team members trying them out in their lessons and evaluating their
effectiveness in engaging students. The benefits of this project are,
therefore, two-fold. First, the proposed engaging strategies will be
evidence-based and second, the evaluation study to be adopted by team members
is a good opportunity to enhance their pedagogical research skills. Parkin, D. (2017) Leading Learning and Teaching
in Higher Education. London: Routledge. |
|
6. |
Evaluation of the Revision of the General
Education Foundation Programme |
The
General Education Foundation Programme (GEFP), since its full launch in 2012,
consists of two compulsory courses for all students in CUHK. Through reading
excerpts of selected classics on humanity and nature, in the two 3-unit
courses, In Dialogue with Humanity and In Dialogue with Nature
respectively, the goal is to allow students of different disciplinary
training to have a common intellectual and cultural ground, to discuss upon
the important perennial issues of human civilization. It is designed to help
students acquire and develop knowledge, attitudes and skills that are
essential as an independent learner and to be an educated citizen. After a
decade of successfully running the GEFP, in the 2022-23 academic year, a
revision of the programme that re-orients it towards the needs of the
students in the upcoming decades is to be conducted. This revision is one
part of the implementation of the “CUHK 2025” strategic plan. More
specifically, the revision of the programme includes the following key
changes: 1.
Increased
emphasis on the teaching of sustainable development goals 2.
Increased
emphasis on the teaching of the fundamental role of language 3.
Reduced
number of core texts to allow more in-depth discussion and reflection on each
text 4.
Enforced
consistency on the medium of instruction and the written assessment 5.
This project proposes to develop the necessary tools
for evaluating the effectiveness of the two courses, and
then evaluate whether the revision can lead to the expected outcomes. Three
types of data (perception, behaviour and
performance) will be collected from two types of stakeholders (teachers and
students). It is intended that findings will better inform curriculum review,
pedagogical designs, instructional strategies, and course implementation for
enhancement purposes for the GEFP and for the university. |
|
7. |
Further Development and Evaluation of the
Core Courses on Computational Thinking and Digital Literacy |
· As defined by Wing (2006) in her seminal
paper, computational thinking encompasses the knowledge, skills and attitudes
necessary for solving problems by drawing on the basic concepts of computer
science. It has been identified as a 21st century skill,
incorporated in school curricula worldwide and assessed in large-scale
international assessments. In phase with the global trend, CUHK has moved a
bold step forward in revamping the existing core IT course by incorporating
elements of computational thinking as well as digital literacy, which is
highlighted in its new five-year Strategic Plan “CUHK 2025”. · In 2021-2022, the Faculty of Engineering
was tasked to design and pilot two new core IT courses, ENGG1003 and ENGG1004
(Digital Literacy and Computational Thinking - P and R respectively). A trial
evaluation study was conducted, and the two pilot courses were proved to be
effective. However, given that enrolment in the pilot courses was voluntary
and the enrolment number was small, the sample was not free from bias and the
findings had limited generalizability. A more comprehensive evaluation is
necessary for investigating how the two new courses work when they are fully
implemented on a mandatory basis. · Considering the far-reaching impact of
this major curricular change, this project proposes to further develop the
courseware and evaluate the effectiveness of the two new core IT courses in
their first year of full implementation in 2022-2023. Enriched courseware
such as more micro-modules, new IT workshops, improved eLearning and
assessment support systems, etc. will be further developed. Quantitative and
qualitative data will be collected from students and teachers to identify the
feedback, process, outcomes and their relationships. By surveying a whole
student cohort and a newly formed teaching team, it is expected that this
project will further inform the design and implementation of the two new
courses. |
|
8. |
Developing An Online Self-learning Course for CUHK Students to Strengthen Their
Basic and Subject-specific Research Skills
|
The Chinese University of Hong Kong Library (CUHK Library) has been
offering different kinds of workshops and seminars for all levels of
students. Topics include basic research skills, searching e-resources,
managing citations, understanding academic honesty, measuring research
impact, understanding open access & research data management, etc. Given
the trend of online learning and to support the strategic plan CUHK 2025,
CUHK Library developed various self-learning tools for students to learn
independently, such as Research Smart, Information Literacy Online Courses,
and EndNote Online Courses, etc. The coverage of these online courses is extensive. However, these
courses are not connected. They were developed on different platforms and
might not be easy for students to acquire all these essential research skills
in one place with their limited time. The sustainability of these courses is
also a challenge for the library. Thus, it is proposed to develop a new
online self-learning course for both undergraduate and postgraduate students
which will be housed in the Library website for the
following purposes: · To consolidate all learning materials in
one platform only and to update the existing online courses which might be
out-of-date · To enhance learning effectiveness as
students can always review the course content · To enrich the course content by including
new areas · To allow students flexibility in terms of
timing This initiative is proposed to develop an independent online course
with at least four modules: · Module 1 – Basic Research Skills · Module 2 – Subject-specific Research
Skills (8 subjects) · Module 3 - Managing Citations for Your
Research (EndNote and RefWorks) · Module 4 – Publishing your work (optional
for UG students) Features of
the proposed online course: · Independent web-based course developed by
a courseware development tool · For both CUHK undergraduate and
postgraduate students · Participants will be required to log in
before accessing the course · Supplementary · 4 modules (self-paced) · 45 mins of estimated reading time per
module · Step-by-step instructions · With animation and instructional videos · Learning activities and exercises will be
embedded to check their understanding · Pre-module & post-module surveys for
evaluation purpose This new online self-learning course is targeted to be launched in
Term 1 (2025-2026). It would be opened to all CUHK students. Upon request by
teaching staff, this online course could be specifically modified and
embedded in their curriculum as part of the assessment. · |
|
9. |
Interactions and Active Learning in the New
Normal: uReply for Blended Learning |
In the past TDLEGs, we
launched and then provided a campus-wide service called uReply. The solution
has a strong pedagogical focus to achieve active learning through
facilitating various types of interaction using the mobile technology. The
system has not only attracted impressive popularity among teachers at CUHK,
over the years, through effortful continuous development, uReply has also
been extended into not only a classroom tool but also a tool for asynchronous
interactions, game-based interactions, and location-based interactions. It
has proven to be an important tool for virtual teaching and learning as well
during the pandemic and it is compatible with innovative pedagogy such as
flipped classroom and self-directed learning. The present TDLEG application seeks resources to 1)
continue the running of the service with a growth of user-base in mind, and
2) further develop the tool to meet the needs for the future especially to
support the new needs related to blended learning. To support blended
learning, more teaching and learning activities should be able to be
conducted effectively online and thus we propose to enhance features include
the following. Assessment is an important component that requires
more and more online support in the blended era. During the TDLEG 19-22,
uReply developed an assessment component as a means to
support asynchronous interactions, we propose to further enhance this
component so that it supports the university strategy to apply criterion
referencing. Criterion referencing in assessment is a university policy but
the marking of assignment using this approach usually requires the use of
marking rubrics that adds a great deal of workload to teachers. The
rubric-based assignment marking tool will be integrated to Blackboard as well
such that teachers can use either uReply or Blackboard to collect their
assignments. The new function will work well in the blended environment as
the submission, marking and dissemination of the marking are all accomplished
on a mobile-ready interface over the Web. Blended
learning requires responses from online systems to be smarter and
individualized. The supervisor has recently received an IICA grant to work
with five other universities to explore AI in education. The new initiative
is a community-of-practice type of projects and with the purpose to network
pioneering teachers and developers across the universities and share as well
as teach each other various AI applications in education. An important
follow-up action side-by-side the project is to implement AI-related
enhancement into uReply. For example, we are optimistic that the auto-marking
technology can be used in many parts of the system, such as to analyzing the
classroom interactions as well as the assessment submissions. Chatbot and
other NLP/ object recognition functions will be useful in giving more support
to students with SEN. A revamp of the look
and feel of uReply is needed to consolidate the functions we built over the
years. Since many of the functions are developed by different programmers in
the past, they do not look and behave like a single platform. Another goal of
the upcoming revamp is to better unite the whole system. For example, a
single login process will be provided, such that students do not need to log
into another session number when teachers shift to another interaction
sub-tool in uReply, such as from an anonymous to the login-required mode. We
also take this opportunity to unify teachers’ and students’ user experience
no matter it is an in-class or online learning environment for more
comfortable blended learning. |
|
10. |
Teaching and Learning Community of Practice
(T&L CoP): Consolidation Together with Extension to Address Teachers'
Pedagogical Research Needs |
This proposed initiative seeks to use pedagogical research as the focal point
to expand our existing teaching and learning community of
practice (T&L CoP) for teachers across eight faculties and other academic
units at CUHK. In particular, this timely proposal
will provide periodic and tailor-made pedagogical research support as part of
the professional development for academic teaching staff following a new
institutional policy on widening research participation effective from 1
September 2022. Such a proposal builds
on the strengths of two existing projects, one of which is the Teaching and Learning CoP (evolving
from the eLearning CoP established in 2017) and the other which is the Virtual Teaching and Learning (VTL)
Pedagogical Research Service (established in 2021). Previous work has
laid the solid foundation for this proposed initiative in two significant
ways. First, we have successfully developed a structured CoP with
approximately 100 active
and like-minded teachers and the multifaceted research support service model. The second
significance coheres around the viable transfer of existing collaboration
networks and opportunities as well as lessons learnt from our current/recent
work to this proposed project. The new project intends to provide
professional development support to enhance teachers’ teaching and learning
practices and to possibly translate their best practices through research. |
|
11. |
The Impact of Universal Design Learning
Model on Inclusive Education at CUHK |
Quality
education is important to groom all students in the tertiary educational
environment. To achieve quality
education, we have to ensure inclusive and
equitable quality education to all students.
Therefore, the readiness for teachers at CUHK to cultivate an
inclusive study environment to all students is crucial. The current study will evaluate the
understanding of inclusive framework in Universal Design Learning (UDL) in
terms of growth mindset, self-efficacy, self-regulation, and motivation for
the university teachers in CUHK. This proposal aims to establish a one-stop
interactive platform for teachers at the university with a view to increasing
their awareness of UDL in supporting students with or without Special
Education Need (SEN), as well as communicating and sharing their experiences
in accommodating these students. A series of workshops will be organized to
promote the UDL framework. The micro-modules will be generated on the webpage
as learning materials for teachers. Two evaluation surveys for teachers and
students will be conducted to evaluate the UDL inclusive practice in the
university with a view to establishing an inclusive campus environment. We
also recognize the teacher support to SEN students. Most of the studies in special education
examine the learning needs and support of students with SEN, but fewer
studies investigate teachers’ beliefs and attitudes toward inclusive
education such as their mindset toward students with SEN, their teaching
efficacy, self-regulation when confronted by students, as well as their
motivation in teaching students with SEN in higher education. Therefore, the current project also
evaluates the impact of UDL on the changes of teacher’s mindsets and the
support to SEN students. |
|
12. |
Students-as-Partners (SaP)
Model in Teaching and Learning at CUHK |
Students’ participation in teaching
development is one of the important strategies in
the CUHK Strategic Plan 2025. Involving students-as-partners (SaP) in teaching and learning development is an essential
strategy that encourages students to take bolder steps in their learning.
The traditional SaP approaches have been developed
and applied in the Western context.
Nevertheless, it may not be fully applicable in the Chinese teaching
and learning environment. Therefore,
the current project aims to develop a SaP model at
CUHK. The
present study will focus on the evaluation of existing practices in SaP at CUHK. Furthermore, it
is significant to address the barriers in curriculum
design and difficulties in collaborative teaching and learning throughout the
process of
implementing SaP. Therefore,
this proposal
aims to periodically
update and enriches the SaP platform, for teachers at the university with a view to increasing their
awareness of SaP
in supporting teachers. A series of workshops will be organized to promote
the SaP framework in teaching. The micro-modules
will be generated on the webpage as learning materials for teachers. Two
evaluation surveys for teachers and students will be conducted to explore the
SaP practices in the university with to establish
teaching and learning partnerships at the university. Five exemplars of SaP curricula will be developed as the exemplar in this
proposed project. Therefore, the current project also evaluates the impact of
changes in teachers’ mindsets and students’ skills and competencies. |
|
13. |
Pedagogical and Assessment Support for
Service-learning Programme |
Being emphasized in the CUHK 2025 Strategic Plan, Credit-bearing
Service-Learning Programme (CSLP) will be promoted and incorporated into the
undergraduate curriculum as compulsory requirement by 2024-2025. To
facilitate the Colleges and Departments to develop credit-bearing SL courses,
continue preparing teachers and faculty members with sufficient SL knowledge
is of utmost importance in promoting SL as well as integrating different
ideas of SL into credit-bearing courses. The current proposal is focused on
supporting the curriculum design and practices of SL courses in the
university. The objectives of this proposal include (1) the evaluation and
optimization of the current SL platform; (2) the investigation on the CSLP to
be offered by all nine Colleges in the upcoming two school years; (3) the
development of a CUHK SL assessment rubrics for the College credit-bearing SL
programme; and (4) the establishment of University-Community collaboration
for SL. |
|
14. |
Academic Advising Support for Teachers at
CUHK |
Effective academic
advising (AA) is, without doubt, an important part for CUHK students in their
tertiary education. The current AA system in CUHK was developed a decade ago.
We have conducted a study adopting qualitative and quantitative approaches to
evaluate the AA system at CUHK by interviewing over 712 students and 36
teachers in 2020. A workshop was hosted by this project’s principal
supervisor with around 40 teachers participated
in 2021 April. Teachers expressed several concerns over the AA system which
are related to the (1) support given by the university, (2) a lack of
examples or experience sharing by other advisors. They are eager to advance
their AA skills to establish a solid relationship with their advisees. To
address this issue, the current proposal is to produce a full package for
teachers to follow when doing AA. The package includes (1) an
interactive webpage, (2) Guidance tips for advisors to follow, (3) series of
workshops with experience sharing session of advisors. |
|
15. |
AI at the Forefront: Charting the AI
Landscape at CUHK |
Artificial intelligence (AI) is rapidly transforming higher
education, with significant implications for teaching and learning. To
effectively integrate AI technologies into teaching and learning practices,
it is crucial to understand the knowledge, perceptions, attitudes, and
applications of AI among students and teachers. The findings will shed light
on the current AI policy for teachers and students of CUHK. This proposal
outlines a comprehensive survey targeting teachers and students to gather
insights into the needs and concerns of the university community regarding AI
technologies. The survey serves to enhance pedagogical effectiveness and
student learning outcomes. A key deliverable of this project is developing a
survey instrument that can measure and review continuously and sustainably.
the university's AI policy, practices, operational procedures, and
stakeholders' responses towards it This instrument will enable datadriven decision-making, facilitate benchmarking, and
contribute to the broader field of AI in education research. The survey's
findings will inform policies and strategies to integrate AI in a relevant
and inclusive manner. By proactively assessing and addressing the challenges
and opportunities presented by AI, this project will enhance the university's
teaching and learning activities, drive innovation, and ensure sustainable
benefits for the institution and its constituents. |
|
16. |
AI in Academia: Training and Capacity
Building for Teachers in Higher Education |
The proposed " AI in Academia: Training and Capacity Building
for Higher Education Teaching Staff" programme is a pilot initiative
designed to empower CUHK faculty members with the necessary skills and
knowledge to effectively integrate AI and Generative AI into their teaching,
research, and curriculum development. This programme, developed based on
benchmarking similar courses provided by overseas and local universities and
comments from an external reviewer, specifically focuses on the practical
application of these technologies within pedagogical settings in higher
education, ensuring that educators are not only familiar with AI concepts but
are also proficient in applying them to enhance their teaching methodologies
and research activities. Central to this programme are hands-on workshops structured to
demonstrate real-world applications of Generative AI. These workshops allow
teachers to experiment with and adapt these tools to suit their educational
contexts best. By engaging in these practical sessions, faculty members can
gain confidence in handling AI technologies, facilitating a smoother
transition of these tools into their everyday teaching and research
practices. Upon completing the programme, participants will receive certificates
that reflect their expertise and accomplishment in integrating AI into their
professional practices. These certificates serve as a testament to their
skill development and a catalyst for further professional growth, motivation,
and enhancement of the educational quality they deliver. By establishing a
benchmark for AI competency among the university's teaching staff, this pilot
initiative lays the groundwork for a broader application and acceptance of AI
technologies in higher education, setting a precedent for future programme
expansions. |
|
17. |
Developing Academic Staff Members'
Pedagogic Research Engagement at CUHK |
This proposal aims to enhance academic
staff’s engagement in pedagogic research by actively creating learning
and interactive opportunities. We intend to achieve this through three key
initiatives: scaffolded professional development, knowledge exchange, as well
as networking and collaboration opportunities. Specifically, the notions of scaffolding
and active construction of opportunities play a pivotal role in these
proposed initiatives, as mere attendance does not automatically translate
into practice. Therefore, our scaffolded professional development will
adopt a sandwich approach which draws reference from the feedback sandwich
(Ash, 1984). It will consist of pre-workshop reading groups, main workshops,
and followed by post-workshop group consultations. The topics covered in
professional development workshops will include various research
methods/methodologies and key concepts, such as mixed-method design,
participatory action research, creative methods, rigor/trustworthiness, and
reflexivity. Pedagogic research (PedRes)
knowledge exchange will be manifested in the form of sharing sessions
which emphasises collaborations with external partners and academics from
beyond Hong Kong higher education. This exchange will enable the university
to tap into the latest innovative practice and global perspectives in
education. A networking event, namely a facilitated writing retreat,
will be organised to enhance teachers' academic productivity and
collaboration. It is worth noting that the identification of the three areas
of needs for pedagogic research support mentioned above is based on 83 valid
responses collected in a current study on pedagogic research engagement at
the university (Reference No. SBRE-23-0201). This proposal will complement
our ongoing work on developing a teaching and learning community of practice
at the university, while cultivating academic staff’s capacity for pedagogic
research and fostering a collaborative pedagogic research culture within the
university and beyond. |
|
18. |
Integrating AI in Assessment for Learning
Enhancement & Grading Efficiency |
Traditional
assessment methods suffer from biases, inconsistency, and time constraints,
hindering effective teaching and learning. The project aims to enhance
teaching and learning activities at the University by integrating generative
AI into the assessment process. The benefits of AI integration include swift
grading, objectivity, scalability, personalised
feedback, and analysis of student learning patterns. However, technical
barriers such as input format complexities and prompt engineering pose
challenges. To address
these challenges, the project aims to develop a user-friendly and adaptable
platform that can accommodate specific assessment needs. The platform will
empower educators, including those with limited technical skills, to leverage
AI as an assistive tool to enhance grading efficiency and learning
effectiveness. The system
development is consisted of two phases. Phase 1 involves research and
development focusing on interface design, AI model selection (e.g.,
ChatGPT4.0), and rubric interpretation integration. Phase 2 will consist of
pilot tests in diverse settings, followed by feedback collection for
refinement. |
|
19. |
Postgraduate Academic Advising Support at
CUHK |
Effective academic advising (AA) is a
crucial part of the tertiary education experience for CUHK students. In the
recent UGC Quality Audit Report, the comprehensive academic advisory system
at CUHK was confirmed. Yet, the guidelines and resources to support effective
AA for postgraduate students are currently lacking. To address this issue,
the current project aims to evaluate the needs of both research postgraduate
students (RPgs) and academic staffs in conducting
academic advising at CUHK. In addition, the current project also empowers
academic advisors in engaging academic advising activities to RPgs. The project will be based on the Self-Determination
Theory (SDT) to design surveys for all RPgs and the
faculty who supervise them, in order to: (1) conduct a survey to both
teachers and students in assessing the needs during academic advising, (2)
prepare Postgraduate Academic advising guidance tips for the academic
advisor, and (3) produce micro-module and organize several workshops to
empower academic advisors to RPgs’ academic
advising needs. |
|
20. |
Advancing Sustainability Education at CUHK
and Beyond via General Education and Cross-sector Synergy |
· This proposed project aims to enhance
sustainability education at CUHK at large, making it one of the core
strengths of CUHK’s educational excellence. · Embracing social responsibility for
sustainable development is a key component of CUHK Strategic Plan 2021-2025.
To this end, a strong focus on sustainability education is essential, and
CUHK’s leading role in and contribution to the education and pursuit of the
United Nations (UN) Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) are envisioned. · The General Education (GE) curriculum has
contributed significantly to broadening our students’ intellectual horizons
to meet the global SDG challenges. An SDG Study Scheme was launched in
2020-21 for the systematic development of sustainability education within GE
in CUHK. · To advance SDG education across and
beyond CUHK, we propose to revise and expand the SDG Study Scheme and extend
sustainability education beyond GE to reach all students and teachers in
CUHK. The targets at various levels include: o
University
GE: Revising and
expanding the SDG Study Scheme; supporting experiential learning for SDG-GE
courses through SDG Experiential Learning Activity Fund; o
GE
Foundation (GEF) Programme:
Incorporating and evaluating the effectiveness of one new classic reading on
sustainability as a common-core text in GEF, to help all CUHK students
develop a keen appreciation and sense of urgency to live and work in harmony
among economy, society and environment; o
College
GE: Incorporating SDG
elements in College GE courses and establishing synergy between the SDG Study
Scheme and College service-learning programs; o
Faculties
and University:
Developing a university-wide SDG course inventory to help students design for
themselves and teachers to advise on a sustainability-focused education;
analyzing the landscape of sustainability education across CUHK; organizing
engagement workshops and building a Community of Practice on Sustainability
Education across faculties; o
Beyond
CUHK: Participating in
Hong Kong Sustainable Campus Consortium (HKSCC) for cross-institutional
collaboration; organizing SDG Forum Series for students and the general public; collaborating with international
university and industry partners in the “Future17” program. |
|
21. |
An Online Bilingual Glossary in Support of
Language Alignment in General Education Foundation (GEF) Classes |
From the academic year 2022-2023 onwards, students in the General
Education Foundation (GEF) classes will need to adhere to the language
alignment policy of the University, which requires the language of written
assignments to correspond to the language of classroom instruction. This new
policy will pose three kinds of intellectual challenges to students. First,
students in Chinese-medium classes, constituting 80% of the total, will need
to expand their Chinese vocabulary related to the intellectual concepts
articulated in the core texts. Second, in expressing their understanding of
the texts (mostly written in English), students will be confronted with the
task of finding the appropriate Chinese terms to encode the relevant
concepts, based on a refined understanding of their subtle meanings. Third,
as students have to read core texts related to both
humanity and nature, the lexicon they need to master covers a broad range of
conceptual domains. We propose to build an online bilingual
glossary of the GEF core texts with a three-fold objective: (a) to provide a
convenient tool to search for the translation equivalents of key terms
encountered in the core texts; (b) to provide easily accessible information
on the contexts of use of the key terms by the author, with reference to
etymology and word formation; and (c) to engage students in the enrichment of
the glossary and the development of this eLearning platform. |
|
22. |
A Mentor-assisted Study Scheme (MASS) |
·
After being implemented for ten years, The General
Education Foundation Programme, comprising the two ‘dialogue’ courses (“In
Dialogue with Humanity” and “In Dialogue with Nature”) is facing two challenges. Firstly,
students’ encounter with the classical texts is limited in time, depth and
scope. On average teachers and students devote only three hours per week to
each work, which in most cases is a short excerpt. Secondly, due to the
intricacies of the concepts introduced and the complexity of the language
that encodes them, many students find it difficult to develop an in-depth
understanding of these texts. ·
We propose to make full use of Virtual
Teaching and Learning (VTL) to launch a Mentor-assisted Study Scheme (MASS),
aiming to enrich and upgrade the learning experience of CUHK students with
the support of the wider university community. The scheme will include: (i) a management web platform that provides academic
resources and organises hardware resources; (ii) Classics reading
groups, with small groups of students led by mentors who are
faculty members, alumni, or College tutors; (iii) Student book-review
sessions co-organised with the University Library; (iv) Podcasts hosted on
the MASS platform for students to share their reflections and insights gained
from the book reading experience. |
|
23. |
Developing An Inter-faculty
Collaborative Experiential Program to Foster Students’ Science Communication
Skills |
·
In
the 2019-22 triennium, we have developed a science communication partnership
program between the School of Life Sciences (SLS) and the General Education
Foundation Programme (GEF) to train SLS students to become science
communicators and lead GEF students, who are of diversified majors, to
perform scientific investigations. The project puts strong emphasis in
encouraging students to become partners in curriculum and teaching. ·
In
this triennium, we propose to extend this partnership program to Earth and
Environmental Sciences Programme (EESC) and Department of Geography and
Resource Management (GRM); to substantially enhance the science communication
training; and to strengthen the experiential workshops provided to GEF students, taking into
account the curriculum reform of GEF, pedagogical
considerations and students’ feedback. ·
During
the proposed project period, 40-60 senior SLS, EESC and GRM students will
receive the science communication training
and oversee up to 720 GEF students to perform scientific investigations. For SLS, EESC and
GRM students, the skills
that they learn align well with the graduate attributes of the University.
For GEF students, participation in the workshops and a written reflective
worksheet will become part of the assessment of the course. ·
Quantitative
and qualitative methods will be employed to evaluate the success of the
project, including online survey, focus group interview, and textual analysis
of written reflections. ·
The
proposed project well aligns with the strategic development direction of the
University outlined in CUHK2025. It also increases students’ awareness of the
United Nations Sustainable Development Goals. The project can be extended to
other sessions of GEF courses and applied to other CUHK programmes
and courses that aim at fostering students’ skills of communicating
professional knowledge to non-technical audiences. |
|
24. |
A Compendium of Introductions and Reading
Guides to the Revised Course Books for In Dialogue with Humanityand In Dialogue with Nature |
To enhance the General
Education Foundation (GEF) Programme, the teaching teams of “In Dialogue with
Humanity” and “In Dialogue with Nature” have recently revised the list of
classical texts for the two courses. We propose to write a compendium of
introductions and reading guides for the new set of classics which will form
the core of the GEF curriculum from the academic year 2023-2024. In a programme which requires students to read and reflect on
classics, the list of selected texts embodies and codifies the
educational ideals of the course planners. The current revision represents a
continued commitment to engaging students with perennial issues of human
existence, as well as an added emphasis on language and sustainability, in
response to the call of our times. The success of a course, however, depends
not only on well selected content, but also on the delivery of it. The
compendium addresses the needs of delivery. The existing teaching materials in support of the two reading
intensive courses, compiled at early stages of the GEF program, suffer from
noticeable deficiencies when looked at with hindsight. The teaching notes
were developed by individual teachers as isolated, disparate efforts to help students
overcome the difficulties posed by a small number of texts. The materials are
by and large outdated or fragmentary;
they do not incorporate the lessons that we have learned from our teaching
practice over the last decade, and provide only
partial coverage of the texts. The proposed compendium of introductions and
reading guides will represent a
collective, integrated effort of GEF teachers in pedagogical enhancement.
The compendium will be comprehensive
in covering all the required texts. It will be systematic in its approach, aiming to standardize the design, format and pedagogical content of the
teaching materials. These aspects of the delivery are deemed essential for
enhancement in the teaching of the GEF courses. In the University’s initiative to revamp GE, we see the GEF
Programme as being entrusted with a more active and interdisciplinary role in striving to attain its learning
outcomes by training students to articulate their understanding of the
classics and their thoughts more effectively, through intensive reading and
writing, adopting a “Language across the curriculum” approach in collaboration
with the Department of Chinese Language and Literature and the English
Language Teaching Unit. The compendium will be a product of such
interdisciplinary efforts. To ensure that the compendium meet high academic standards, experts
and scholars will be invited to special seminars and symposia to share the
state-of-the-art research on the relevant classics. As a concerted,
systematic, comprehensive, and interdisciplinary effort by a group of veteran
GEF teachers trained in different disciplines, the compendium will combine
current scholarship with the pedagogical insights of GEF teachers. The
project will consolidate the teaching of GEF and serve as a concrete demonstration
of the unique educational philosophy and pedagogy of GE at CUHK to the wider
public. |
|
25. |
Developing an AI argument recognition tool
for a KeyWord-in-Context-based method to assess
students' understanding of specific concepts |
For courses with large numbers of
students and essay writing assessment components, it is both highly desirable
and not easy to quantitatively estimate, from students’ essays, to what
degree they, overall, have acquired a more detailed and accurate understanding
of specific concepts, or developed more comprehensive and logically
consistent argumentation skills. This is certainly the case of GEFP courses.
In this regard, one of the Principal Supervisors (K.C.) has developed a
method for quantitative analysis based on the computational linguistics concept of KeyWord-in-Context. Such a method can provide clear
non-subjective indications for individual teachers' pedagogies and for
evidence-based pedagogical research. Promising preliminary results from a
sample of about 700 essays from 7 academic terms, have been presented at the
ESERA 2023 international conference and at an internal conference of the
GEFP. The aim is to develop an AI framework
that allows teacher-users to train a machine to recognize specific statement
or argument types, so as to speed up the most time consuming step in the
implementation of the KeyWord-in-Context method of
analysis. The project is intended to be only the
first stage of development of what, through a second longer stage of
development, should become an end-user ready software tool. |
|
26. |
Consolidating Peer Learning at CUHK for
Synergy and Furthering Development |
· At CUHK, a variety of
peer learning and tutoring opportunities are enhancing the academic and
social engagement of students. The Peer Assisted Study Sessions (PASS), in particular, has demonstrated remarkable effectiveness
in elevating academic performance, enhancing self- efficacy, and fostering a
sense of community. To build on this success, a new initiative aims to
consolidate these efforts through a Special Interest Group (SIG) under the
CLEAR’s Community of Practice (CoP) framework. This will allow for a more
inclusive and synergistic approach to peer learning, encouraging exchange and
learning among educators using diverse models. · The project is
designed to complement the ongoing TDLEG project, focusing on the transition
support role of PASS and the development of scholarship around peer learning.
By collecting baseline data, raising awareness, establishing a platform for
exchange, identifying stakeholders, and supporting the implementation of peer
learning, the initiative seeks to create a systemic impact on CUHK’s
educational landscape. · Key to this effort
will be forming the SIG, conducting a comprehensive survey, hosting
workshops, offering a PASS Supervisor accreditation program, and developing a
website to showcase peer learning opportunities. · The ultimate
goal is to sustainably integrate peer learning across CUHK,
underpinned by its proven effectiveness in not only improving grades but also
fostering vital affective outcomes that contribute to long-term student
success. The project members have received the University Education Award
2021 for their work, and this project seeks to further advance on that
foundation of achievement. |
|
27. |
Designing and Implementing a Technical
Framework for Credit-Bearing Courses at CUHK |
Online credit-bearing
courses have become prevalent in higher education institutions because: · Many students prefer taking online
courses that allow them with greater flexibility
· Elementary and introductory courses can
be held on the KEEP online platform, so that teachers put more focus on
advanced, face-to-face classes The number of online
credit-bearing courses currently hosted by KEEP has increased significantly,
from 3 courses in the academic year of 2021-22 to 10 courses in 2022-23. In
view of the increasing demand for online credit-bearing courses, it is of
utmost importance to improve the
functions of the KEEP platform and the integration services between KEEP and
CUSIS so that: · The
university will benefit
from the development of online credit-bearing courses on the KEEP platform
with higher efficiency on administration tasks · Teachers and
administrators can
exchange course information on KEEP, such
as course enrollment, student status and records, completeness for courses,
and more. It will also provide better support for teachers to deliver their
learning materials online, and assess their students’ performance in class.The integration of KEEP
and CUSIS allows teachers to submit the course grades of their students using
the KEEP platform. This can help them increase their productivity and save
time for inputting the students’ data on CUSIS · Students
can have a more effective
channel of acquiring new skills and knowledge |
|
28. |
Course Recommendation and Course Optimization System for Lifelong
Learning |
Problem
KEEP is an e-learning platform
that provides free online MOOC courses for over 150,000 users worldwide (https://course.keep.edu.hk). According to the statistics
in September 2022, KEEP provides over 173,000 courses online, and the number
is expected to surge in the coming years. At the same time, we are collaborating with various partners
regionally and globally, such
as GDHKMOCC “粵港澳大灣區高校在線開放課程聯盟”, to provide high-quality online
education to learners. While there are
hundreds of thousands of online courses on the KEEP platform, it raises
another problem for our learners – how can they choose the right course for
themselves? In addition, how can we ensure that the platform encourages
knowledge acquisition in different disciplines and provides the best
educational resources for learners in a user-friendly manner without
requiring them to use additional time and effort to seek out the educational
resources that are most relevant to their
needs? Idea
To tackle the problem, we plan
to: · Recommend courses to students through the use of algorithms and machine learning · Make sure students fully understand the
course objectives before they enroll · Offer suggestions to teachers for
writing course descriptions so that they can attract students who have a
genuine interest in their courses Execution
To execute the proposed ideas,
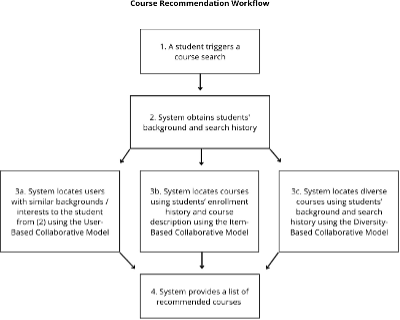
we will take the following actions: · Course
recommendation system This system helps
learners save a significant amount of time when selecting their courses
on the KEEP platform. The system will use machine learning technology to
analyze students’ background, academic interests, and level of understanding
of a certain discipline and recommend courses that best suit their needs. The
new system will cover students at not only CUHK, but also global users on the
KEEP platform. · Insights
into writing course descriptions The system can also offer suggestions for writing better course
descriptions so that teachers can find the right students to enroll in
their courses. It analyzes the course metadata and provides invaluable
insights for teachers regarding the background of students who are admitted
to their courses. 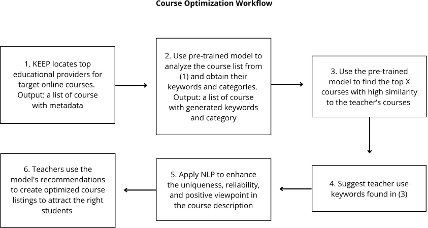
|
|
29. |
The Readiness of Metaverse in Pedagogical Approach for Tertiary
Education |
Metaverse or extended reality (XR) is a burgeoning field that
provides a constant digital space enabling multiuser to have social
networking virtually with enhanced physical reality. XR hardware is a handy,
stand-alone immersive device, user-friendly, and affordable tool for allowing
users to the XR terraforming platform. Moreover, XR can reconstruct an entire
teaching and learning environment to continue knowledge delivery and skill
training if there are any unexpected lockdown measures in the community. In
future education, XR may be widely adopted as a mobile computer to provide
immersive learning experiences to sustain quality enhancement in teaching and
learning flexibly anytime, anywhere, with teleporting communication and
interaction. This project involves teachers and students from several local
institutions, including CUHK, HKU and HKUST. This proposed project aims to
formulate key universal educational opportunities and the environment by the
affordances of XR technology, identify the novel challenges of XR in the
future meta-education crossing the geographical boundaries in the virtual
world and share experience in XR pedagogical strategy with stakeholders in
the community of practice. This proposed project will plan for the
multidisciplinary approach with XR visibility-aware simulation entitled
"Metaverse Educational World-Land (X-Land)", which will
develop comprised of three elements 1) XR 360o first-person
perspective skill training; 2) XR serious game training simulator, and 3) XR
networking theatre to set up the universal social netting virtual environment
among the curriculums. With the research study for the proposed project, our
team can explore if the paradigm shift can adopt innovative pedagogies for
continuous teaching and learning enhancement to other programs and courses. |
|
30. |
Sustainable Tourism Planning Games for
Cross-disciplinary and Territory Knowledge Sharing and Student Engagement |
Aim ·
This
university-level project develops a tourism
planning game for engaging students from different disciplines and territories to advance the
understanding of destination planning and the
all- important Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) through knowledge
and case sharing. Brief
Project Description ·
This project creates two online
role-play games (one
rural context and
one urban context; both English and Chinese versions) for tourist destination
planning based on the SDG framework and a collection of real-world case
studies from students of the project team members. Students in
CUHK will be highly engaged in
the game development process. ·
Overall game flow: First, student players are assigned to a particular role under public
sector, private sector, civil
society or local
community, and their
respective goal to achieve – maximize certain
SDG scores. Second, the players must study their goals and resources
in hand, and conduct rounds of one negotiation with other roles in exchange of resource
cards (e.g. forest cover, endangered species, land, capital, local culture,
etc.). Third, after completion of 10 rounds, the game will determine the
winner by summarizing the available SDG scores and resource cards.
One additional parameter will be taken into consideration – a global sustainability in
economic, social and environmental status that affects the game result.
Details of game design will be refined by student engagement process. ·
The
game is constructed on a hypothetical destination
but the roles and conditions are a collection of real-world topics such as ecological conservation, indigenous and
community empowerment, social and cultural exchange, stakeholder relations,
tourism impacts and management, which are all common and inter-disciplinary
knowledge areas in sustainable tourism. Teachers may utilize the game as an in-class or online teaching activities to enhance teacher-student and peer interactions. Significance ·
This project is of high
relevance and beneficial to facilitate students to cross knowledge boundaries through the acquisition
of knowledge in different disciplines, student
engagement, game-based and experiential learning. There will be
cross-university and cross-territorial constructive long- term advantages
when the game is utilized continuously across project team members. ·
The
project significance is four-fold:
(1) inter-disciplinary knowledge acquisition and sharing, (2)
cross-university and cross-territory teaching and learning enhancement, (3)
student engagement in game development, and (4) advantages of game-based
learning for in-class teaching and virtual interface. ·
The
university-level initiative is developed from previous game-based project
outcomes of the Principal Supervisor. This new project further widens and
deepens the scope of teaching
collaboration and long-term utility
of the game
across courses and institutions, which
supports and showcases the
sustainability of university-level collaborations. |
|
31. |
Enhancing Follow-up Learning Experience by
Leveraging “Topic Guidance Enquiry Framework” on Guided NLP Model for
Tailored Student Engagement |
In every
lesson, after specific topics have been taught, in
order to provide better support, we require few enthusiastic teaching
assistants to interact with students individually. Their role will involve
identifying students' weaknesses, asking topic-related questions, and
providing feedback or additional exercises. However, it is not feasible to
have sufficient manpower to guide each student on a one-on-one basis. This project
aims at developing a pedagogical assistive platform that utilizes the Topic
Guidance Enquiry Framework as a backend engine to generate a Guided NLP
model. The Web APP will empower university-level teaching staff to
effortlessly generate tailor-made prompts using the backend framework engine.
It will also include shared URLs of NLP models, such as POE or chatgpt, that those prompts will be deployed to
complement students' post-lesson learning journey. It can enhance student
engagement and improve learning outcomes. Teaching
staff will be able to send students the URLs of the guided NLP models after
teaching specific topics of the course. This will enable students to receive
personalized questions in a structured sequence. The model will assess their
background knowledge, prompt them to explain detailed concept, encourage them
to provide step-by-step processes and ask them for listing examples from
their own experiences related to the subject matter to gain insights based on
their individual strengths, weaknesses, and areas of interest. After that,
the model will assign a knowledge level score based on students' responses
and provide extra suggestions and resources accordingly. These resources will
be available in various formats, including links to related websites, downloadable
PDF readings and publicly accessible videos. Finally,
pedagogical research encompassing methodology, expected outcomes, and
experimental results, including statistical analysis, will be conducted
involving university teachers and students from the Engineering, Art,
Science, and Business faculties. This
initiative is expected to benefit more than 800 students. The specific course
offerings that will be the focus of this research are as follows: Engineering
Courses: ENGG1130 -
Multivariable Calculus for Engineers (Capacity: around 500) ELEG3701 -
Embedded Systems Design (Capacity: around 50) ELEG2201 -
Digital Circuits and Computing Systems (Capacity: around 50) Art Courses: TRAN1010A
Principles of Translation (Capacity: around 40) TRAN2070
Introduction to Translation Studies (Capacity: around 40) Business
Courses: DOTE1040
Macroeconomic (Capacity: around 70) DOTE2011
Statistical Analysis for Business (Capacity: around 70) Science
Courses: CHEM1072
General Chemistry (Capacity: around 60) UGEB2420A
Chemistry in the Kitchen (Capacity: around 60) CHEM1280B
Introduction to Organic Chemistry and Biomolecules: (Capacity: around 30)
|
|
32. |
Communicating Capstone: Hosting the CUHK
Capstone Project Presentation Contest and Creating An
Online Space for Capstone Presentation Showcases |
Academic literacy
represents a wide range of abilities that students have to
acquire when they pursue a new academic discipline. The awareness that
successful performance at university requires students' mastery of academic
literacy is particularly important in second language environments such as
Hong Kong, where difficulties that they encounter in academic pursuits tend
to go hand-in-hand with a lack of competence in
English (Wingate, 2018). In CUHK,
all undergraduate programmes ensue the systematic
inclusion of a capstone component as the culmination of students' four-year
academic study, which targets the synthesis of their subject knowledge,
independent inquiry or execution, as well as problem-solving and other
generic skills (CUHK, 2022; CLEAR, 2017). Typically, a capstone extends over
the final 12 months in the form of research or a final year project, whereby
students ultimately submit a final report or thesis through which capstone
supervisors assess their overall learning outcome. In this
connection, various learning needs arise - to best communicate their capstone
experiences to target audiences in different discourse communities, students
will need resources and support in acquiring relevant language skills. While
efforts have been made to cater for student needs in acquiring specific
discourse practices and academic communication conventions (Hyland, 2017) in
different major disciplines, there is also a growing global trend on making
academic research and understanding accessible to a wider audience (e.g. 3MT,
TED, FameLab). This calls for the establishment of
a space for students to showcase their projects to a broader audience outside
of their major classes and sharpen their communicative skills with guidance
and support from language educators. The proposed project aims: 1) to provide a
university-wide platform that offers students an opportunity to showcase the
outcomes of their year-long capstone projects to a much wider audience 2) to enable students to
present research work in their chosen academic disciplines effectively to non specialists in a concise and engaging manner 3) to equip students with
communicative and language skills necessary for goals #1 and #2 through
providing training and coaching 4) to build an online
showcase space to host a collection of student capstone presentation videos
from various academic disciplines/ faculties and house relevant language
learning resources 5) to give capstone
supervisors and academic advisers of major programmes/departments/faculties
access to exemplary student presentation samples of various forms of capstone
projects as an additional teaching resource in the future |
|
33. |
Enhancing Learning through Diversity at
CUHK: Reaching Multidisciplinary Tech Partnerships Program (RMTPP) |
This
proposal introduces a Reaching Multidisciplinary Tech Partnerships Program
(RMTPP) that aims to forge connections between international and local
students by working on collaborative projects focused on community care
solutions. The program encourages students, from different backgrounds to
form teams and use their unique skills to address challenges in biomedical
engineering. These teams could develop products like a smart walking stick
for the elderly or a brainwave device for improved sleep, or design software
and AI platforms for public health issues such as mosquito-borne diseases in
Bangladesh. The RMTPP goes beyond traditional learning by using the POP
(Performance-based assessment in Open-ended Problem-based learning) approach,
which promotes creative thinking and social impact. It is open to students
from all faculties of CUHK. Key elements of the program include cultural
exchange, interdisciplinary training, and developing communication and
teamwork skills. Participating students will gain insights into innovation
and career prospects, receiving a certificate upon completion. The
implementation involves forming pairs of international students from
disciplines who will be guided by professors, in conceptualizing and
implementing solutions. We expect this initiative will enhance learning
experiences and promote STEM education for the Hong Kong community. |
|
34. |
Building An Inter-institutional and
Inter-disciplinary Community-engaged Learning Hub: Baccalaureate Education
for Social Good (BESGO) |
This
project is a continuation and expansion of ‘Business for Social Good
Education’ (BESGO), a project funded by TDLEG 2019-22. BESGO was a big
success and has been well-received by both internal and external
stakeholders*. While several students were granted internship after
participating our activities, some has decided to embark the journey to
further explore the field of social good. Therefore, the project team would
like to expand the project to benefit a greater group of students from all
faculties and cover social good on both business and other disciplines.
This
project focuses on both theoretical and practical aspects of three
interrelated areas: social innovation, social good, and ESG ("Focused
Areas”). Specifically, the project aims to: 1.
Raise
students’ and general public awareness on various social needs and challenges, sustainability issues and
shared value creation; 2.
Deepen
student’s understanding on social innovation, social good and, ESG, and how social enterprise and industries can
address social needs and be a force for good; 3.
Advocate
concepts and practices relevant to CSV, CSR, ESG to larger audience to drive system level changes; 4.
Encourage
students to participate in activities with positive social impacts and
integrate sustainability consideration into daily lives decision; and 5.
Serve
as a platform to connect local and international partners to work together on
our focus areas to provide students with exposure and opportunities to create impact. Not only
will students develop a structural and holistic understanding of the Focused
Areas via a series of well-structured training workshops conducted by
international, inter-disciplinary academics from local and overseas
institutions and industry practitioners, they will
also learn directly from social change-makers in talks and field visits. The
project team has liaised with 3 strategic partners, namely, HKPC, SVhk and SVIHK and a number of
local and international institutions to form partnership. More importantly,
students will be given opportunities to conduct guided corporate projects
under the supervision of faculty members and practitioners to put what they
learn into practice to create real impacts to society. The
project contributes to multiple University’s themes, namely, (1) Promotion of
attitudes and values, (2) Development of community-engaged learning, (3)
Development of professional and generic skills, (4) Encouraging students to
make contributions to society as citizens & leaders, (5) Contribution to the United
Nation Sustainable Development Goals, , (6) Facilitating students to cross knowledge
boundaries through the acquisition of knowledge in different disciplines and
(7) Encouraging inter-institutional collaborations. * Please refer to the project report for
‘Business for Social Good Education’ supported by TDLEG 2019-22. |
|
35. |
Empowering Global Student Teachers for
Transformative Teaching and Learning in a Globalized World |
Aim of the Project ·
The
aim of the project “Empowering Global Student Teachers for Transformative
Teaching and Learning in a Globalized World” is to provide student
teachers with the necessary skills and knowledge to excel in diverse
educational contexts. Through this cutting-edge initiative, student teachers
will be equipped with the tools and expertise required to thrive in a rapidly
changing globalized world. Structure of the Project The Project is conducted in a cross-regional, cross-institutional
teacher education programme, where students (pre-service teachers) directly
participate in a wide range of learning and teaching activities, covering: ·
Four
immersive local thematic workshops in collaboration with the Museum of
Climate Change (MoCC), Ocean Park Hong Kong, Hong
Kong Wetland Park, Coral Academy, and The Nature Conservancy Hong Kong
(TNC-HK), centered on marine conservation. ·
Three
dynamic Virtual Thematic Pedagogy Workshops designed for student teachers and
in-service teachers to enhance their virtual teaching skills and navigate
online intercultural learning environments. ·
Four
impactful Global Curriculum Planning Sessions featuring synchronous club
meetings focused on UN SDG14 (Life below Water). This inclusive initiative
involves preservice teachers, international university students, and middle
school student groups from at least five countries. ·
Engaging
global participation through four specially curated lessons for middle school
students (aged 10-13) worldwide, providing valuable teaching experience for
student teachers. ·
Weekly
reflection meetings for preservice teachers to openly discuss and exchange
successful or challenging leadership moments, fostering collaborative
learning opportunities. ·
Development
of a progressive e-Learning Platform for Global Education, facilitating the
sharing of students’ reflective posts, digital stories, workshop outlines,
and valuable insights with stakeholders. |
|
36. |
Enhancing the Teaching and Learning of
Engineering Research Writing with a Specialised
Corpus and Corpus-informed Resources |
Rationale:
University students and language instructors in English for Specific Purposes
(ESP) and engineering courses often struggle in teaching and learning
engineering-specific discourse/expressions due to lack of command as well as
training/resources. Language acquisition research has shown that one of the
best ways to acquire language – e.g., discipline- and genre-specific
vocabulary and expressions – is through context/situated learning. However,
it is difficult to implement such tasks without materials that put language
in context, or materials that can be designed as tasks in the language
classroom. The use of corpora, or structured language databases, is an
optimal solution, as it can achieve both of these
simultaneously. There are existing corpora, but the ones available for
engineering are small in scale, private or outdated. Aim: This
project aims to (1) develop a contemporary large-scale specialised
corpus of academic writing for engineering studies (CAWES), (2) creating
pedagogical word and collocation lists and lists of common expressions, and
(3) constructing an online concordancer to support
materials (re)development and self-access learning. Approach: The
approach involves developing a genre-specific specialised
corpus of 5 million words, consisting of peer-reviewed research articles from
reputable publishers across various engineering sub-disciplines – the
standard of engineering-style English writing. The corpus will be annotated
to enable nuanced analysis and extraction of textual data for pedagogical and
research purposes. Outcomes and impact: The project will lead to the creation of CAWES, which is expected to
inform curriculum and materials development in relevant courses and support
students’ self-access learning. In terms of research, CAWES has the potential
to contribute to our understanding and conceptualisation
of genre and style in corpus linguistics and sociolinguistics research. Its
availability can also lay the groundwork for research opportunities in ESP,
vocabulary and writing. |
|
37. |
An AI-enhanced Adaptive and Individualized
eLearning System for Mathematics Foundation Courses in the Faculty of
Engineering |
As
mandatory courses to all undergraduate engineering students, mathematic
foundation courses are essential to engineering education. However, the
teaching materials in standard mathematic courses cannot fully meet the
students’ multifarious personal needs. Especially, there lacks
of sufficiently appropriate exercise questions for students at various
learning levels. This issue seems growingly perilous in online mathematic
education under the pandemic. This
project aims to develop an AI-enhanced elearning system in teaching mathematic foundation
courses, to meet the students’ customized learning needs at different
learning levels adaptively, as an auxiliary
system to the existing standard and unified mathematic education in the
Faculty of Engineering. The basic idea is that students will be dynamically evaluated by an elearning system on different contents in learning mathematics, and
personalized appropriate teaching materials will be supplied via this elearning system, which is formed via an Artificial
Neural Network model trained by Cognitive Development Optimization Algorithm. The objectives of this project includes: 1) An AI-based elearning system is expected to be built, where
personalized teaching materials could be provided adaptively. The perspective elearning system consists of
two main components, i.e., iTest and iLearn. 2)
Through the sub-system iTest, students could
be dynamically evaluated and classified at different learning level,
on sorted contents of mathematic courses. Students, on the other hand, could
obtain self-fitting exercise questions based on their learning levels. 3) According to the evaluated learning level of each student, the sub-system iLearn furnishes with substantial and suitable learning materials, like
supporting reading references and illustrating examples, in which students
could further strengthen their understanding of mathematic concepts and
theorems regarding their learning level. The perspective AI-enhanced elearning system will demonstrate its effectiveness in existing mathematic courses: ENGG1120 Linear Algebra for Engineers and
ENGG1130 Multivariable Calculus for
Engineers with more than 600 students who are expected to benefit from
this project. |
|
38. |
Hands-on Robotics Course Modules for
Interactive Self-Learning |
Self-learning refers to providing
students with material or opportunity to learn without the help of another
people, such as the course teacher and assistants. Traditionally, this comes
in the form providing students with reading material, videos, homework
exercises and assignments. These contents can be performed by the students
either before (flipped learning) or after classes
(revision/reading/homework). However, as these contents are mostly non-interactive,
the motivation and effectiveness for students to use and learn from
self-learning material is typically perceived to be low. From our previous endeavours and
successes in transforming traditional lectures to hands-on robotic lectures,
this project aims to develop a set of self-learning modules for learning
robotics that are hands-on and interactive. These modules are all-inclusive
to allow the students to self-learn, containing theoretical introduction and
explanation of concepts, hands-on exercises with instructions and assessment
with feedback. Different to existing types of self-learning content, our
proposed content will be centred around the interactive use of a robot arm,
rather than simply reading or calculation exercises. Students will be able to
interact with our learning content in two modes: 1) in-person with the robot
arm while wearing virtual or augmented reality glasses; and 2) through our
online robot simulation platform. Moreover, the content will be used both for
flipped learning and after-class supplementary material. The developed modules will be based on
different topics and themed robot application examples, making it both
interesting and suitable to be used within different robotics courses within
the Faculty of Engineering. The team will also explore collaborating with
local and non-local universities such that the material can be beneficial to
robotics students beyond CUHK. |
|
39. |
Teaching Avatars: AI-Powered Video
Summaries for Lecture-Based Courses |
The
explosion of AI in the last two years promises profound opportunities for
pedagogical advancement in higher education. This project seeks to leverage a
number of those tools in order to create a simple
workflow for academics that will allow them to provide effective video
summaries of their lectures to students. The tools used include AI-powered
lecture transcription, AI-powered summarization, and AI-powered video avatar
creation. Rather than having to laboriously create a series of micro-modules
for the purpose of aiding student revision of complicated material outside
the classroom, this project will demonstrate that with relatively little
training academics can rely on commercially available AI tools to provide
those same benefits with much less effort. |
|
40. |
Blended Learning UGE Course on United
Nations Sustainable Development Goals and Health |
· Drawing
upon the success of the past triennium with the TDLEG-funded eLearning course on United Nations
Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and health, the objective of this
project is to extend and enrich the educational experience of students
through virtual and face-to-face blended learning in a University General
Education (University GE) course. · Adhering
to the UGE criteria, the SDG blended learning course fosters problem-based
learning with case studies and group projects. The course places
strong emphasis on intellectual ideals, breadth and connectivity and will be
based on solid learning outcomes. · Since
SDGs are global goals directed towards the promotion of peace and prosperity
for people and the planet, the course fulfills the desired characteristics of
University GE in relating to human experience and modern life. · In
alignment with the CUHK Strategic Development Theme of ‘CUHK 2025’ in
promoting “excellence with a deep sense of purpose and responsibility”, the
blended learning course coupled with teaching and learning enhancement
provides an effective and wide-reaching method for knowledge dissemination. · The
course reinforces key areas suggested by UGC for TDLEG 2022-25 which is to
deepen virtual teaching and learning (VTL) adoption. It will link up with
CUHK’s university-wide SDG initiatives and encourage inter-institutional
collaboration. |
|
41. |
Impact of Interprofessional Education on Teachers’ Mindsets and
Students’ Competency and Graduate Attributes |
The current project aims to evaluate the impact of
inter-professional education (IPE) on students’ holistic competency and
graduate attributes at the Chinese University of Hong Kong (CUHK). This project is line with the CUHK
strategic plan 2025 and the United Nation sustainable development goals
(SDGs) to goals 3 (good health and well-being), 4 (quality education), 10
(reduced inequalities), 16 (peace, justice, and strong institutions) & 17
(partnerships for goals). Based on our
previously TDLEG funded project on IPE, we confirmed that students welcome
IPE at CUHK. Nevertheless, the most
feasible faculty that could apply IPE would be the Faculty of Medicine. Therefore, the current project will focus
on the IPE development from the Faculty of Medicine perspectives. This project involves three phases. Phase 1
is the establishment of IPE website at CUHK. The website will provide
supporting evidence, pedagogical designs, and assessment related to IPE. The purpose of the website is to promote
IPE at CUHK. In phase 2, we aim to evaluate the impact of IPE on student’s
skills, knowledge, and competencies. The final phase is to evaluate the
impact of IPE on teachers’ and students’ attitudes and values after
implementation of the IPE project in the community and the relationship with
promoting positive education at CUHK. |
|
42. |
Development of Professional Putonghua for
Medical and Healthcare Settings |
Given the strategic plans of CUHK 2025 and the
position of Hong Kong’s excellence in education, there is a need to enhance
the professional medical Putonghua language skills of public health and
medical students who already have a strong foundation in Putonghua. This is
to meet the needs of an increase in Putonghua speakers in Hong Kong, as well
as the professional development needs of Hong Kong healthcare professionals
for interprofessional collaboration and exchange with mainland doctors in
working and leadership development in the Greater Bay area. Currently, there
are limited resources in learning medical Putonghua. The course and materials
developed in this project will provide advanced medical Putonghua training
and insight into the mainland healthcare environment. This will encompass
advanced medical Putonghua classes, roleplays with Putonghua speakers,
seminars with physicians and nurses, and e-learning resources. This course will be open to all Faculty of Medicine
students, including nursing, medical, and public health students. Research
into the professional use of medical Putonghua, e.g. mainland healthcare
forms, health reports, case discussions, etc., can set a foundation to
develop an assessment that will test learner’s listening, speaking, and
writing skills. A library of audio, visual, and written resources will also
be developed. |
|
43. |
Enhancing Teaching and Learning of Medical
Professionalism |
Medical students are expected to learn the concept
of medical professionalism to maintain their trust from society when practising medicine after graduation. A previous study
from our University demonstrated the adverse effect
of the hidden curriculum created by the negative role models in the clinical
teaching environment. Teaching development programmes
on medical professionalism should be designed for clinical teachers to
convert the harmful hidden curriculum into a positive one. Medical students must submit reflective writings
regularly during different stages of their medical professionalism learning
track as assignments. All the reflective writings are substantial
student-initiated teaching material that can be used to supplement the
existing learning programme. We proposed to produce a teaching and learning
enhancement programme for the medical professionalism teaching in the Faculty of medicine as follows, ·
Teaching
development programme – Polishing the hidden curriculum Three e-learning micromodules 1.
Individual level. 2. Organisation level 3. Clinical
vignettes related to different specialties ·
Learning
enhancement programme– Enriching the feedback for the pre-clinical medical
students Three e-learning micromodules
using qualitative analysis of reflections submitted by students about the
introductory concepts of professionalism: 1. Professionalism, 2. Code of
conduct and social media, 3. Public health professionalism ·
Learning
enhancement programme – Enriching the feedback for the clinical medical
students Three e-learning micromodules using qualitative
analysis of reflection submitted by students about advanced concepts of
professionalism: 1. Conflict of interest, 2. Truth-telling, and 3. Role
modelling. Face-to-face conclusion lecture to debrief the
understanding of professional identity by comparing the result of the
qualitative analysis of their reflections in pre-clinical and clinical years We expect the teaching development programme to
abolish the unprofessional culture in the clinical learning environment
created by clinicians involved in undergraduate teaching so
as to nurture tomorrow’s doctors’ professionalism to safeguard the
society’s wellbeing. The learning enhancement programme will engage the
students as learners and teaching partners in medical professionalism
teaching. |
|
44. |
Interdisciplinary Blockchain Education: Development
and Deployment in the Faculties of Law, Medicine and the Business School |
Disciplinary
faculties of Law, Medicine and the Business School all recognise
the need for equipping graduates with skills to meet the practice of the
future. This includes discipline-based teaching of emergent technologies such as blockchain, which will have
a profound impact
on graduates’ future
lives and professions. At present, each Faculty is individually
developing teaching of foundational concepts and discipline-specific aspects.
This project will establish an interdisciplinary teaching team to create a
‘core’ set micromodules on blockchain fundamentals for all three faculties,
as well as interdisciplinary modules and discipline-specific cases in this
critical technology. The
project will adopt an innovative pedagogy for the online micromodules:
dialogue-based education. Departing from the
traditional narrated monologue, we will incorporate dual-teacher dialogue in a ‘video podcast’ style to generate a lively learner
experience, illustrate key
points and facilitate interdisciplinary debate. This format further allows adaptive
teaching through a ‘common feedback’ approach,
where student questions from all three faculties are collated and addressed
by follow-up discussion video- podcasts by teachers. Finally, each faculty
will supplement the micro-modules with case-based classroom discussions to
enable legal, financial and medical use cases to enhance student learning. Our collaborative practice will form a cross-faculty
infrastructure for the teaching of future emergent subjects. |
|
45. |
"CHIM3DERA" – An Interactive
Student-lead Dissection Workshop and a 3D Scanned Specimen Model Platform to
Enhance Interdisciplinary Peer-learning of Anatomy and Acupuncture |
· Recruitment of students from Medicine and
Chinese Medicine Programmes in dissection workshops to participate in
student-oriented interdisciplinary peer-learning in Acupuncture and Anatomy. · Enhance students’ understanding of
state-of-the-art in Traditional Chinese Medicine healthcare practice:
Acupuncture, with fundamental Anatomy knowledge through human dissection. · Maximize the benefit from “Silent
Teachers Body Donation Programme - CUHK” in local medical teaching in university*. · Student
group presentation with 3D-scanned prosected specimens illustrating precise acupoints with
surface anatomy and underlying human structures. · A web-based platform archives all 3D
scanned models, annotated multimedia videos/photos could be implemented as advanced teaching materials for current undergraduate and postgraduate courses, “Human Structure” (MED), “Meridian System” and
“Acupuncture” (ChiMed). · Sustainable development of the project
could further promote knowledge transfer at inter- universities,
university-community levels to enhance practical skills and refreshment of
knowledge of healthcare practitioners such as physicians, registered Chinese
Medicine practitioners and physiotherapists who practice acupuncture. * Bachelor
of Chinese Medicine in CUHK is the ONLY
UGC-funded programme with dissection-based learning Anatomy and
Acupuncture among all local universities. |
|
46. |
Enhancing Empathic Ability and Moral
Awareness in Bioethics Learning: A Case-based Approach |
Bioethics
I, II, and III, covering a wide range of ethical topics in medicine, public health, end-of-life
care, and biotechnology, are offered to 819 pre-clinical (Years 1, 2, and 3) medical students in a six-
year undergraduate medical degree program. The current teaching methods for
these courses include both lectures and tutorials for small group
discussions. Medical students in pre-clinical years, however, often
neglect the importance of developing moral
awareness and empathic abilities essential
for their future careers. In the absence of clinical experience, students are
incapable of linking bioethical theories and knowledge taught in class to the
clinical context. Previous
feedback through Course and Teaching Evaluation (CTE) has consistently
revealed that students generally are more interested in learning bioethics when doing so by analyzing real-life cases.
Extensive use of case discussions can help students to develop ethical
problem-solving skills, preparing them for
complex social dynamics present in clinical scenarios. The current
teaching cases, however, are
outdated, and were developed predominately in Euro-American contexts. This project will
produce an up-to-date, scenario-based, and modified real-life case collection, largely from the local context, for each module in the bioethics courses offered in pre-clinical
years. The deliverables include: 1) A casebook of 20-40 cases that contain
case descriptions, ethical questions and/or concerns, and commentaries,
largely from the Hong Kong context, in both online and hard- copy formats; 2)
three scenario-based micro-module videos in end-of-life care-related topics. |
|
47. |
Development of an Innovative eLearning
Package to Facilitate Learning of Radiographic |
In the
acute care setting, lines and tubes play important roles in supporting or
maintaining life or normal health functions. Malpositioning,
coiling, kinking, fracturing, or malfunctioning of lines and tubes are not
uncommon, but unfortunately not easily detected without adequate training and
experience. Additionally, peri-procedural complications are significant, but
often not immediately apparent clinically. Radiological evaluation immediately after the
placement of a range of medical lines
or tubes is now recommended in many institutional
guidelines, to evaluate for malposition or
complications. In
undergraduate training of the next generation doctors, nurses, and healthcare
practitioners, greater emphasis needs to be placed on the radiological
identification of lines and tubes and their complications, to reduce this
major cause of preventable morbidity and mortality. This
project proposes to develop an integrative eLearning package to facilitate
student learning of radiographic assessment
of lines and
tubes and their
potential complications. The
project encompasses technology in education with
implementation of artificial intelligence (AI) deep learning and game-based
learning, as well as a mobile application (app) platform to integrate the
eLearning package. These technologies promote student learning whilst also
enriching radiological education with up-to-date advances in the field
(through AI), and facilitate undergraduate teaching
of engineering students in programming and
AI. We build
on our past experience with developed eLearning
modules of a similar nature for nasogastric tubes. In this project, lines and tubes
covered include: percutaneous central venous catheters, Port-a-Caths, Hickman lines, peripherally inserted central venous catheters (PICC
lines), endotracheal tubes (ETT), tracheostomy tubes, intercostal catheters,
drains/pigtails, biliary related tubes, amongst others covering the range of
commonly encountered lines and tubes. We aim to
cross disciplinary boundaries with the proposed educational package which can
be used for teaching across multiple departments, schools and faculties.
Building on our past close collaborations and prior work, the project team
encompasses teachers and students as partners in teaching material development. |
|
48. |
Virtual Reality-Based Interactive Simulator
of Clinical Teaching (VR-ISCT) for the Assessment and Management of Medical
Patients |
· COVID-19 pandemic and hospital infection
control present major
challenges to medical education. Students' access to
patients are restrict, limiting their exposure to wide spectrum of medical
conditions. Clinical skills have deteriorated as a result. · We have developed an
online Interactive Simulator of Clinical Teaching (ISCT) platform using
real-life cases with their recorded heart and breath sounds through which
medical students could appreciate clinical signs in a safe environment.
Although majority of medical students were satisfied and considered the
platform useful, an online platform could not replicate real patient
encounter experience. · Virtual reality (VR)
based simulations are increasingly used in medical education to provide cost-effective, immersive, repeatable training on demand in a safe environment
via autonomous and blended learning. · We aim to build upon
our existing ISCT platform by (i) developing a
fully immersive and interactive VR environment that includes audio, visual
and pseudo-haptic elements to enhance learning experience and (ii) expand our
real-patient case library of commonly encountered cardiovascular and
respiratory conditions. · Our VR platform will
allow more cases and other examination systems (e.g. neurological, abdominal
and rheumatological etc etc.) to be added in the future. · Project will target a
wider audience including medical and nursing
students. |
|
49. |
Implementation of Interprofessional
Education with Team-based Simulation Training and Online Interactive
Discussion |
Background: Following
the emergence of the COVID-19 pandemic, clinical practicum for health
discipline students has been inevitably affected or even suspended,
especially high-risk areas such as accident and emergency department and paediatric unit. Interprofessional education (IPE) has
high pedagogical values in education for healthcare professionals.
Simulation-based IPE can provide conducive learning environment and authentic
learning experience. Aims: To conduct
IPE in the modality of simulation training and online interactive discussion
for medical, nursing and pharmacy students, and evaluate its effects on
interprofessional collaboration, perceived self-efficacy and readiness for
IPE. Methods: A total of
20 simulation scenarios involving emergency, paediatric
and medical and surgical clinical situations for IPE will be developed with
inputs from medical, nursing and pharmacy students. A total of 200 bachelor students studying Year
4 to 6 (40 medical students, 40 nursing students and 20 pharmacy students) will participate in the
simulation-based IPE in simulation wards or online interactive discussion. Students will collaborate and exercise their
skills in communication, coordination and teamwork. Debriefing will be conducted to consolidate learning issues. Outcomes will
be evaluated by a mixed-method approach. The effects of interprofessional simulation and interactive discussion will be reflected by students’ attitudes towards
interprofessional collaboration, perceived self-efficacy, readiness for IPE
and satisfaction with simulation experience. Students’ learning experiences
will also be explored. Conclusion: This
project will provide students with opportunity to engage in the development
of teaching and learning activities for IPE.
The results will provide directions and suggestions for effective
implementation of IPE in the faculty and University, and
inform curriculum development. |
|
50. |
Integrating Ophthalmology Education in
Multiple Specialties with e-learning Materials, Interdisciplinary
Collaboration, and Service-Learning Opportunities for Medical Students |
Background: The CUHK MBChB curriculum consists of a
1-week ophthalmology rotation. Students are assessed by an end-of-rotation
quiz without requiring further assessment in the final examination. They tend
to find it difficult to engage in the rotation and to retain the knowledge
because of the limited teaching time, minimal exposure, lack of repetition,
disconnection with other core specialties, and the rotation tend to teach
from a specialist ophthalmologist perspective, which could be irrelevant to
the students’ future practice (given that most of them will practice in other
medical specialties). To address these challenges, we propose integrating
relevant ophthalmology knowledge into teaching other medical specialties,
allowing early exposure to the knowledge, and bridging the knowledge gap
between different subjects. Methods: Based on the success of our new
flipped-classroom case-learning (FCCL) ophthalmology course – which consists
of pre-class teaching videos, gamified cases, and in-class case-based
learning – we aim to expand the learning outcome by integrating ophthalmology
components into other specialties (family medicine, internal medicine, and
paediatric) and provide opportunities of early exposure. This will include 1)
real-case interactive e-learning materials, 2) interdisciplinary
collaboration, 3) optional student-initiated extra micro-modules, and 4)
optional service-learning opportunities. Students are exposed to new
e-learning ophthalmology materials that are based in the context of other
core specialties during the earlier year of MBChB. They can then revisit the
material during the ophthalmology rotation (final year) and learn in an
ophthalmologist context. We will also include videos of patients and parents’
interviews to aid in learning communication skills and understanding the
biopsychosocial aspect from a different perspective. We will also include
ophthalmology content related to internal medicine to aid students’ final
exam preparation. Students can also initiate extra tutorials with the project
supervisor. We will also work with external collaborators (e.g., ORBIS,
Jockey Club) and students could join our departmental community services,
sharing sessions with secondary school students, public health talk, and
charity work. This
combination can achieve 1) fun learning, repetition, and application of the
core knowledge, 2) enhancement of student-teacher interaction, 3) motivating
self-learning and enhancing students’ autonomy, and 4) application of
knowledge and skill to serve society. The effectiveness of the
project will be measured by student scores in the post-course and post-MBChB
assessment, Likert scale questionnaires, and qualitative-translation impact
assessment. Potential: This model could extend to other specialties
in the CUHK MBChB curriculum and other courses in CUHK. We aim to promote this
concept and model to other university departments and local educational
institutions of all levels. |
|
51. |
Development of AI-Powered Virtual Patients
for Healthcare Education |
Driven by
the rapid development of technologies that generate artificial intelligence
(AI), the integration of AI in healthcare education is emerging. AI-powered
virtual patients have become an important application in the training of
students in healthcare discipline. This project
involves collaboration between teachers from different departments and
different local institutions, including CUHK, PolyU,
and HKU. Its objective is to develop voice-based, AI-powered virtual patients
that include scenarios from different clinical specialties, such as medicine,
surgery, pediatrics, emergency, and critical care. By employing AI and our
non-identifiable data sets that captures patients’ socio-demographics,
medical history and diagnoses previously used for teaching and learning purposes;
the AI-powered virtual patients provide students with opportunities to
interact with replicas of “virtual patients” who respond in unpredictable,
human-like ways. It also designed to provide students with opportunities to
comprehensively assess and identify the problems of AI-powered virtual
patients and thereby implement appropriate interventions. This allows
students to practice a wider range of real-life scenarios virtually before
managing patients in the real world. Through
research studies, our team will examine how this paradigm shift can extend innovative
pedagogies for clinical teaching and enhance learning across various courses
and programme. |
|
52. |
Development of virtual interactive
micro-modules on public health crisis management and risk communication |
After the pandemic, the need for effective crisis management and risk
communication cannot be overemphasized. This project aims to create virtual
interactive micro-modules to address public health crises including, but not
limited to, infectious disease outbreaks. These modules are developed
according to principles in the crisis management framework for health system
put forward by Emami et al. emphasizing on preparedness, resilience building
and learning from past experience. They will equip
undergraduate students in the health discipline with essential skills to
navigate complex situations and effectively communicate essential information
to the public. The built-in virtual scenarios would require students to make
real-time decision based on risk assessment, prevailing principles and
guidelines, and ethical considerations. According to the World Health
Organization’s framework for contingency planning, effective crisis
management hinges on cross-disciplines collaborations. The modules are
multidisciplinary incorporating elements of field epidemiology, communication
strategies, behavioral models and policy considerations. Students will learn
strategies to handle and tackle misinformation and promote evidence-based
information. Case studies from the COVID response will serve as valuable
teaching materials. Project objectives: · To develop interactive virtual
micro-modules that engage students in realistic scenarios related to public
health crises and risk communication · To equip students with practical skills
in crisis management, risk communication and ethical decision-making Key features of the
micro-modules: · Pandemic Scenarios · Real-Time Decision-Making · Multidisciplinary Insights drawing from
epidemiology, communication studies, behavioral psychology, and public
policy. · Addressing Misinformation The project aligns with the
following goals: · Development of Professional and Generic
Skills · Enhancing Global Readiness of Students · Encouraging Students to Make
Contributions to Society as Citizens or Leaders · Deepening Virtual Teaching and Learning
(VTL) Adoption · Harnessing Innovative and Breakthrough
Technologies for Teaching Development · Contribution to the Sustainable
Development Goals (SDGs) By integrating real-world pandemic experiences into the curriculum,
we aim to empower the next generation of health communicators and crisis
managers. Other than public health students, the micro-modules will be open
to all Faculty of Medicine students including medical and nursing students.
The innovative learning resources may also be shared among local and overseas
institutions to benefit more students in the health discipline. |
|
53. |
Virtual Teaching Series: Faculty
Development in Managing Complexities in Health Professional Education |
Background: The faculty
of medicine encompass medicine, nursing, pharmacy, chinese
medicine, biomedical and public health students and teachers. There is a need
for teacher development so that they are update with the current issues and
teaching pedagogy, ultimately improving teaching performances that lead to
better learning outcomes for our students. Method: We aim to
developing a Health professional education teaching series which has monthly
asynchronous and synchronous online components. The format includes
pre-session material, online discussion sessions with sharing from expert
speakers, and post session assessment and reflections. These are based on
pedagogy including peer learning, reflection and case problem-based learning. Outcomes: The expected
outcomes include: • Monthly
online sessions with focus topics and key points, case sharing by speakers,
group discussions; online micro-modules with key learning resources • Community
of Practice established in health professional education • Webpage
dedicated for health professional education |
|
54. |
Interactive Geographic Information System
(GIS) Web App of Campus Plant Learning in CUHK |
1.
The
proposed GIS-based interactive campus plant learning platform enables the
good utilization of CUHK campus plants as teaching and learning materials. 2.
A
GIS plant learning platform will be constructed, containing 100 selected
plant species in CUHK. A factsheet would be created for each species with
detailed description of their characteristics. The habitats of the plant
species would be filmed by a 360°
camera. 3.
This
new platform could enhance teaching and learning effectiveness in the
University by promoting students’ self-learning motivation. 4.
This
platform acts as a supplementary tool for plant learning and as a
consolidation of field study. 5.
This
platform could be released in the semester of AUG 2023 as a pilot scheme and
operates for further teaching enhancement in coming years. |
|
55. |
Dr. Ray's Wonderland of Virtual Reality
~the Olympic Games for Science, Biolab Safety and Animal Ethics Education |
Gamification
refers to the use of game design elements for non-game applications. It has
recently been used in science education to enhance students’ motivation and
promote learning. The teaching of biosafety concepts and animal ethics in
large class is traditionally conducted through lectures. Game- based cooperative learning is often
difficult to be implemented in lecture theatre. Therefore, engagement
of students is limited and their learning
effectiveness is generally lower than that of an active learning classroom.
For laboratory safety education, students’ situational awareness and the
capability to solve real life problems in specific type of experiments are
inadequate. With the latest virtual reality (VR) technologies, this project
aims at developing an immersive game-based learning console for foundation
courses with large class size.
The game elements of this learning console include multi-level challenges, user-prompted interactions, role-play, league
tables, multi-media materials and cartoon characters, etc. The console is
composed of 10 situational biosafety challenges in biochemistry and molecular
biology experiments. They are organized into 4 levels of difficulties
according to the complexity of tasks, types of experiments, goals of missions and the biohazards involved. The system
supports multi-players mode that enables collaborative
learning pedagogy. |
|
56. |
Free Generative AI for All: Investigating
the Impact of AI in STEM Education |
· Aim to study the impact of generative AI
in undergraduate STEM educations. · Provide free generative AI service to
undergraduates in the physics and statistics departments. Offer web chat
interfaces with better user experience than typical providers o
Implement
a reverse proxy with caching and recording abilities to enable unlimited
replays of prompts and analysis of student usage. o
Primarily
utilize the open-source Llama 3-70b-instruct model from Meta, ranked 2nd
for English chatbots. Explore local deployment on university hardware or
cloud services like groq.com for cost-effective scaling o
Circumvent
the export barrier imposed by US to ban generative AI in Hong Kong by
exploring local deployment of opensource models and third-party cloud APIs. o
Leverage
and contribute to open-source utilities for model serving, web interfaces,
and other components. · Provide multiple AI services to staff for
benchmarking and comparison in STEM course scenarios. · The project aligns with the university's
strategy of introducing computer skills to students. The python learned in
ENGG1003 Digital Literacy and Computational Thinking course could be utilized
to play with codes generated by AI to facilitate learning difficult STEM
concepts. |
|
57. |
Data-Driven Urban Studies – Advanced
Techniques for Analysing Complex Urban Data and
Processes |
New tools
for the data-driven analysis of urban activities allow us to analyse quality-of-life aspects in relation to the
varying qualities of different urban environments. This project will continue with the development of innovative e-learning resources and teaching methods, related to analytical tools for urban
studies. The first
stage has been completed successfully, after developing a series
of micro-modules and implementing them
within our Urban
Design and Urban
Studies programmes.
The introduction of self-directed virtual
learning in the context of non-formal studio
teaching around specific urban regeneration challenges
in Hong Kong, has led to enthusiastic adoption by students and significant
improvement of learning outcomes. The results are reported in the CUHK
‘Community of Practice Symposium of Education Innovation and Technology’ and
in a paper submitted to the Journal of Planning Education and Research. Surveys and semi-structured interviews amongst students and industry experts have identified several
key areas for further development, including supporting more advanced
data gathering processes, statistical analysis and data visualisation,
and linking data-based research outcomes to planning initiatives conception.
This project extension proposes to develop additional e-learning modules and organise short workshops and seminars targeting the wider
Faculty of Social Sciences and open to all CUHK students. |
|
58. |
Art Technology Design and Culture – Robotics
and Cinematography for Architecture, Journalism and Communications Students. |
Under direction from the Faculty of Social Science, a
cross-disciplinary specialization between Journalism, Communications, and
Architecture departments is being developed. This will bring together the
signature teaching methods found in architecture (design studio), alongside
the specialist skills of communications education – with an emphasis on
technology-driven creative works. The preliminary discussions have found a
variety of common ground, teaching and learning experiences, and great
potential for complementary learning experiences that can enhance respective
disciplines. Tools such as robotics, VR, and computational design tools can
have an important impact in respective professional disciplines. They will
help future proof graduates as they enter the industry as leaders and
experts. This project explores the intersection of journalism, communication,
and architecture education, focusing on the innovative use of cinematography
and storytelling techniques. It posits that these disciplines can mutually
enhance each other, particularly when employing cutting-edge technology such
as robotically driven cameras. The project requires students to gain
awareness of robotic control systems, digitization methods, navigation
between physical and virtual spaces, camera and lighting technologies, editing,
formatting, compositing, and others. The project will also adopt a common 3D
environment (UNREAL), which will serve as the foundation for future projects
involving virtual set design (another common area for collaboration between
the disciplines). UGC SUPPORTED - Journalism and Communications students will gain a
deeper understanding of spatial design and exposure to three-dimensional
geometries for data collection, exploration, and integration into their
productions. UGC SUPPORTED - Architecture students will be exposed to techniques
and technologies that can enhance their ability to tell stories, particularly
about their design works, enhancing presentation quality, narrative, and
illustration through image sequences. Cinematography provides a dynamic medium to communicate architectural
concepts, fostering visual literacy and critical thinking. Robotically driven
cameras offer unique perspectives, facilitating a more immersive exploration
of architectural spaces. Storytelling, a common skill in journalism and
communication, can enhance the presentation of architectural designs, making
them more engaging and relatable. These interdisciplinary skills benefit
architecture students and offer communication students a novel application of
their craft. The fusion of these disciplines can lead to innovative pedagogical
approaches, promoting cross-disciplinary collaboration and broadening the
scope of both architecture and communication studies. This research
underlines the importance of an integrated educational approach in nurturing
versatile professionals capable of bridging the gap between technical design
and compelling storytelling. |
|
59. |
Preparing for An Inclusive Future: An
Age-Responsive Learning Framework for Adapting to Rapid Population Ageing |
Population ageing, stemming from longer lifespans, declining
fertility rates, and the transition of post-war baby boomers into older age
groups, is a prevailing trend in societies. Aligned with UN’s initiative that
calls for actions in promoting healthy ageing across sectors, the programme
prepares students to actively participate in the paradigm shift towards a
more inclusive society. Teaching and learning resources will be developed within the Faculty
of Social Science, benefiting disciplines such as Architecture, Urban Design,
Urban Studies, and Geography and Resource Management, as well as other areas
in the Faculties of Social Science and Medicine. With the adoption of the
Participatory Action Research (PAR) approach, students will engage in
transformative research for/with communities and stakeholders and propose
actionable solutions in their respective fields. Deliverables include virtual seminars for theoretical backgrounds,
interactive teaching materials such as simulation games and action-based
toolkits to enhance student comprehension of scenarios while searching for
innovative solutions, and other learning resources for initiating
community-scale actions such as project pitching and proposal writing.
Students will gain knowledge of the implications of population ageing,
explore the complexities of social issues, and develop social innovation
skills to take action for positive societal impacts.
The project aims to equip students with the knowledge and ability to drive
community-based transition for an inclusive environment for healthy ageing. |
|
60. |
Programming for Humanists Course Design |
This project will facilitate
the development of an innovative course on “Programming for Humanists” that
will be a required part of a new Digital Humanities Minor programme offered
by the History Department. This course aims
to prepare students to undertake collaborative projects in historical and
literary studies by introducing them to specific elements of the programming
language Python not covered in the
core Digital Literacy and Computational Thinking course. These centre
specifically on solving humanistic problems, and
include the use of NLP (Natural Language Processing) and gamification (Ren’Py). By
borrowing techniques from
computer science, this interdisciplinary course will push students to develop
new skills that are useful both for research and in a variety of professional
settings. The project will be
specifically tailored to the type of humanistic research on China in global
context and related topics frequently studied by students at CUHK. With the
assistance of a fulltime RA and SHs, the PI will develop all the materials
necessary for a 13-week 3-credit course, including PPTs, Google CoLab files, problem sets, GitHub profile, etc. For evaluative purposes, these will then be
tested by the SHs who will be surveyed to offer feedback for their
improvement. Their feedback will then
be integrated and the course will then be ready to
teach. This will be followed by
surveys of students in the course. |
|
61. |
Engaging with the Community While at Home:
Online Linguistic Fieldwork in the Greater Bay Area |
Objectives (Four “E”s)
·
To
empower students to take
ownership in learning
how to apply theoretical
knowledge in the practice
of independent empirical research,
i.e., a self-guided investigation of an understudied language from scratch. ·
To enable students to appreciate and support speech communities across the Greater Bay Area (GBA) by
leveraging their linguistic expertise throughout the process
of (i) building
a constructive connection with these communities and (ii) documenting and investigating these linguistic verities. ·
To
enhance students’ awareness of the linguistic diversity of the GBA
with a special focus on three understudied languages: the Siyi (四邑)
dialect
of Cantonese in Jiangmen, the
Meihui (梅惠) dialect of
Hakka in Huizhou, and the Minority She language (畬語)
in Huizhou. ·
To establish a fully
online approach as an alternative to the traditional face-to-face in-person approach in linguistic fieldwork classes. Activities
·
Working as independent researchers, student participants will experience every component of conducting linguistic fieldwork through deep engagement with speech communities, including recruit native speaker
consultants from these communities, prepare for, lead, summarize,
and analyze virtual data collection sessions with them. ·
After the class, PS and CoSs will compile a digital atlas,
compose text outcomes, develop a website, deliver
conference presentations, write journal papers, organize experience sharing sessions, and develop
media coverage. Outcomes
·
GBA’s first online searchable atlas
consisting of digital maps visualizing
linguistic variations. ·
A
collection of student-written descriptions of the
grammar of these
three understudied languages. ·
A practical
field guide featuring questionnaires for documenting
other languages in the GBA. ·
A
website to introduce six methodological
micro-modules of online linguistic
fieldwork. Evaluations
·
“Before and after”
surveys to collect students’ (a)
preparedness and confidence in
application of theoretical
knowledge to independent
empirical research, (b) awareness and appreciation
of linguistic diversity across and cultural/ethnic
recognition of
the GBA, (c) feedback on online linguistic fieldwork. ·
Surveys and interviews to collect
peer instructors’ comments on (a) the validity of the written
outcomes, (b) the practicality of the proposed
methodological micro-modules, and (c) their
willingness to adopt the
online approach in their
future fieldwork classes. Dissemination
·
All project outcomes (e.g.,
atlas, grammar descriptions, field guide,
etc.) will be
digitized and incorporated into a designated
website with free access. ·
The linguistic findings and the
validity of online fieldwork
will be
presented at international linguistics conferences, and written as papers to be submitted to journals. ·
A
students’ experience sharing session
will be held at CUHK,
and news articles and popular
science articles
on this project will be published on traditional media and new media in the GBA. Impact
·
The students will gain firsthand
experience in applying theoretical knowledge to
conduct empirical research while
working with world’s leading experts,
better understanding the
GBA’s linguistic diversity, and
cultural/ethnic bound, and
strengthening their mind in
building a mutually
constructive relationship with the community through their learning process. ·
The project will test and prove the effectiveness of the online approach
in teaching and
learning linguistic
fieldwork, and the methodological outcomes will benefit
other disciplines that involve data collection
through interviews with
human subjects. ·
The involvement of leading researchers from
China and the US not only offers CUHK undergraduate students a more internationalized
and diversified learning experience, but also
establishes a close and sustainable collaboration in both teaching and
research between CUHK and Fudan/UCLA. ·
The study of synchronic dialectal variation
in the GBA enhances our understanding of the diachronic development of local
communities in Southern China, joining in CUHK 2025’s strategic area “China:
Tradition and Modernity”. ·
The media
coverage and the open-access outcomes highlight CUHK’s initiative and commitment in embracing the GBA by focusing on
understudied local languages, aligning with the overarching strategic goal of
the Hong Kong government. |
|
62. |
Identification of Key Aspects in Spanish
Conversation Turn Taking and Giving and Its Teaching |
Big differences in turn taking and giving strategies
in informal conversations exist between Chinese and Spanish native speakers. As a consequence, sociocultural and behavioral errors as
well as message misunderstandings may occur between CUHK students of Spanish
and Spanish native speakers in real life situations. While different
strategies to turn taking and giving have been described and considered in
the design of English
conversation courses, less research has
been done focusing on Spanish and
considering the characteristics
of students of Chinese origin. In this context, some authors are pointing out
the benefits of a direct and explicit teaching approach. This approach can
increase the student awareness of turn taking and giving rules so students
can perform more successfully in real conversations in Spanish compared to
that performance achieved when using mere communicative teaching approach.
The present project aims at proving the advantages of a direct teaching
approach when developing the CUHK students’ informal conversation abilities
in Spanish. For achieving such goal, we focus in some key aspects and adopt a
pedagogical and experimental research strategy that: i)
identifies the real needs of CUHK students of Spanish, ii) describes the
desired learning outcomes for Spanish conversation teaching, iii) defines the
appropriate linguistic, behavioral and cultural contents to be taught while
training students in Spanish conversation,
and iv) measures the learning results of a six-hours experimental Spanish conversation course. |
|
63. |
German Culture and Language Learning in the
Metaverse |
This project aims to create an immersive online
classroom experience for students by providing them with a virtual
environment in which they can interact with each other. The project will
create virtual worlds based on course content and enhance students' learning
through experience. The Metaverse allows teachers and· students to build and
share their virtual worlds similar to online games
such as Minecraft. The virtual world provides an experiential learning
platform where students can deepen their understanding of course content
online. The project aims both at enhancing students'
understanding of German culture as well as at improving their language
abilities. The content of the project will be designed to cater for content
and language courses. For content courses, students will be provided with interactive and authentic tasks
to deepen their
knowledge. For language courses, students will be able to work with authentic
language contexts. Project
idea:
The project will offer a virtual learning environment
for courses of the German program, where students can experience immersive
learning through interactive technologies that promote collaboration and
engagement. Students will enhance their content knowledge and language
skills. KEEP as partner:
KEEP is an e-learning platform that provides online
courses to over 150,000k users globally. KEEP works closely with educators in
the university to integrate the latest technologies into education and
provide immersive learning experiences for students. For more details, refer
to https://keep.edu.hk. Project
objectives:
·
Create an immersive online experience for teaching and
learning German language and culture, where students can communicate with
each other. ·
Boost interaction and engagement among students during
German lessons. ·
Evaluate the effectiveness of the application of
immersive technologies, such as the Metaverse (Metaverse is a network of 3D vi_1tual worlds
focused on social connection) for language and content
teaching at university level. Execution:
·
Based on courses of the German program, interactive
classrooms and a virtual environment will be created where students can
deepen their knowledge of cultural content and German language skills taught
in the actual classroom. ·
Create a virtual
classroom (with
white boards, chalks
and desks, etc .), and a virtual
environment (landscape, buildings, 3D objects, etc.),
simulating genuine experiences which foster interactions and discussions in German and on German culture. ·
Create an
array of interactive activities in
the world of the metaverse, such as
dramas, virtual trips, treasure hunts, etc . ·
Allow students to experience various
interactions through
audio and video
in the metaverse, in which they can
interact about content taught in class. ·
Create pedagogical materials for viewing
and sharing with others,
including video and audio recordings. |
|
64. |
Classics and Cultural Landscapes:
Prioritizing Hong Kong's Classical Literature Corpus and Chinese Opera
Criticism through a Multidisciplinary Digital Scholarship |
· Since 2021, supported by TDLEG funding, the supervisor has developed
two databases that enhance new research methodologies in digital humanities
and serve as teaching tools in classical Chinese literature. · Considering feedback from students and the projected course offerings
of the department of Chinese Language and Literature, this project enhances a
digital database to include a rich collection of classical Chinese literature
and opera criticism, tailored for Hong Kong's educational needs amid the
post-pandemic era. This digital resource serves as a crucial tool for the
exploration of classical texts and interdisciplinary studies. · 1 new database will be produced, 1 existing database will be updated.
With new data that consists of over 300,000 characters, these resources
provide comprehensive access to e-texts of literary works written by Hong
Kong poets and scholars, historical commentaries on classical Chinese music,
as well as corpora of Chinese opera. · The texts are digitized and carefully checked, with name tagging
functions, and a literature map displaying locations mentioned in over 1,800
works by 20th-century Hong Kong poets. ·
The supervisor will organize 2 guided
tours that bring students and teachers to locations mentioned in classical
literary works, enhancing the connection between literary studies and
real-world geographical contexts. 1 journal paper will be published. |
|
65. |
Revolutionizing Elementary Japanese
Education: Harnessing the Power of Artificial Generative Intelligence (AGI) |
This project seeks to investigate the application of Artificial
Generative Intelligence (AGI) technologies, such as GPT, in supporting
elementary Japanese language education. This pilot study will examine the
interactions between AGI tools and educational processes, with potential
implications for future AI applications in foreign language teaching. More
specifically, the proposed project consists of three stages. (1) Initially,
teaching materials aligned with the Japanese Language Proficiency Test (JLPT)
syllabus are developed by the research team. (2) These materials form the
foundational data for training the GPT system. In the second phase, GPT
processes this data to provide feedback on Japanese language outputs from
students at The Chinese University of Hong Kong (CUHK). This feedback is then
analyzed for effectiveness. (3) The final stage involves GPT creating
revision exercises for further practice, with performance assessments
conducted by the AGI system. Through iterative cycles of feedback and revision,
the project aims to refine AGI educational tools, enhancing the teaching and
learning of foreign languages. The findings could significantly influence the
future use of AI in educational contexts, showcasing a transformative
approach to language education. |
|
66. |
Learning Robotics with Mixed Reality: An
Evaluation Study |
·
Robots
are taking an increasingly important role in human lives, and so is robotics
learning in engineering education. According to Tsai et al. (2021), robotics
learning is often achieved by hands-on and minds-on learning contexts which
support constructivist or social constructivist learning. In this regard,
mixed reality (MR) provides an immersive experience which makes situated
learning and transfer of learning possible. Different from augmented reality
(AR), MR allows not only an overlay of virtual objects into the real world,
but also an interaction with and manipulation of the virtual objects. Despite
its increasing popularity, there is a lack of empirical evidence on the
benefits and drawbacks of using MR in robotics learning at higher education
level. ·
Since
2021-2022, the Department of Mechanical and Automation Engineering (MAE) has
introduced an MR platform to project learning in two robotics courses,
MAEG5755 (Robotics) and MAEG3060 (Introduction to Robotics). In 2022-2023,
the use of MR technology will be extended to in-class activities and
out-of-class exercises, i.e., remote laboratory. In view of the
abovementioned knowledge gap, an evaluation study is proposed to investigate
the effectiveness of using MR as an instructional strategy for robotics learning.
Survey and focus group interview data and assessment scores will be collected
and analyzed. It is expected that the proposed project will shed light on
whether and how far this cutting-edge technology could enhance students’
learning experience and robotics education in general. |
|
67. |
A One-Stop Engine for Examination and Item
Analysis Databank (Platform ExMIA) for Quality
Assurance and Enhanced Assessments |
· A well-designed
examination with good quality exam/assessment items can effectively evaluate
students’ understanding of the subject matter, allow benchmarking of
students’ performance with a recognized standard.
·
The
item analysis data generated from the examinations of >50 courses of
different professional programmes coordinated by
the School of Biomedical Sciences represents a resourceful database for the
analysis of students’ performance, verifying the usefulness of the exam items
in evaluating the teaching outcomes, and assuring the quality of the exam
items used are up to the required professional standard. ·
There
is no one-stop solution available in the market that (a) is equipped
with a user-friendly interface for the selection, batch upload/ download of
exam items, (b) allows for sorting, searching and retrieving of exam items,
(c) can effective store item analysis data generated from both online (e.g.
Blackboard, Moodle) and face-to-face examinations. ·
This
project aims at (i) evaluating the effectiveness of
the existing, selected exam item database/ tools (IDEAL, Blackboard and Respondus) for storing exam items and hosting performance
data; AND (ii) developing a one-stop engine that hosts both the exam item
database and the performance data, allowing batch selection, input/output of
exam items and performance data to/from the database. |
|
68. |
Beyond Text-only AI Chatbots: the Digital
Avatar Learning Environment for Human Anatomy |
Artificial
intelligence (AI) chatbots are a promising educational technology, with
scalable potential to personalise education. We
previously developed an AI chatbot for MEDU3300 (MBChB) to support student
learning of anatomy, receiving positive feedback, awards and a journal
publication. To ensure that CUHK remains at the forefront of this educational
technology, we seek to advance and improve our project. One key
feedback from our initial project is that students love the individualised learning and knowledge of the chatbot but
find the text-only interface less engaging. Therefore, this project will
evolve the student learning experience by improving the human-computer
interaction element, transforming the chatbot into a Digital Avatar. An
avatar-based system creates an AI-powered human-like virtual teacher which
can interface with students through multiple avenues including speech, touch-screens and virtual objects. Importantly, we also
advance the pedagogical basis of our AI conversations with a unique origin:
they are now modelled on real video recordings of experienced course teachers
interacting with students, with speech extracted by machine learning and converted to speech pathways for the AI. We will deploy the avatar, built on our AI chatbot
teaching technology, to support over 250 students studying human anatomy in a
dedicated blended learning environment entitled the Digital Avatar Learning
Environment (DALE). |
|
69. |
Interactive Medical History Taking and
Communication Practice for Medical Students Using an Autoresponder Messaging
Platform |
·
History taking is an integral part of medical practice and an important process to help establishing a diagnosis and
formulating treatment. Therefore, history taking and communication skill make
up a core part of medical education. ·
Traditionally, the
teaching of history
taking and communication skill teaching are performed via small group person-to-person workshop, either by inviting real patients or surrogate patients role- played by students. ·
However, The COVID-19 pandemic has greatly limited
medical students’ access
to patients and their chances of clinical skill practice. ·
Most of the history taking teaching follows
a script in which vital
information will be given when a
correct question is asked. This
scripted response can be simulated in text by automatic feedback of the preset response when a
set of keywords are typed. ·
This
automatic conversation generator software (the Autoresponder) can be embedded
into a mobile messaging platform such as Whatsaap
or Messenger which are popular messaging apps that are used widely by current
generation for daily communication. ·
By
incorporating the autoresponder in a messaging platform, medical students can
interact with the autoresponder and practice history taking and communication
skill virtually and on their own. |
|
70. |
Use of Multiple-choice Question Writing to
Engage Nursing Students in Deep Learning and Develop Higher-order Thinking
Skills |
· Students commonly use
surface learning to answer multiple-choice questions (MCQs) in examinations.
Compared with answering MCQs, developing them is an active approach to
promote active learning behaviour and develop
higher-order cognitive skills. · This project aims to
use MCQ writing to engage nursing students in deep learning and develop
higher-order thinking skills. · Approximately 260 Year
3 students will participate in two MCQ writing workshops and they will
develop MCQs in two nursing courses. · Quality MCQs with high
cognitive levels will be pooled to form a student-generated question bank.
Questions will be extracted from the bank to develop revision exercise for
students preparing their examination. · Second round of MCQ
writing will be conducted in the same cohort of their Year 4 study to
strengthen their higher cognitive skills by including clinical experience
gained from placement. MCQs questions harvested in the second round will
contribute and expand the question bank. · A pretest-posttest design will be adopted to evaluate outcomes among the nursing students, including
learning approach, critical thinking, use of higher-order thinking skills in
MCQ writing, quality of MCQs and learning
experience. · The project
is significant to promote students taking ownership of their learning and engage them
in teaching development. |
|
71. |
Developing a Smartphone-based, Interactive,
and Experiential-learning Oriented Direct Ophthalmoscopy Training Module for
Medical Students that Consists of Demonstration Videos, Simulation Practice,
Self-evaluating Instruments, and Innovative Assessment |
Background:
Direct ophthalmoscopy (DO) is an essential skill that could detect critical
systemic conditions that could cost a patient’s life. All medical
practitioners are expected to be familiar with the skill. In practice, direct
ophthalmoscope is underutilised and studies showed
that non-eye specialists generally have poor DO skills due to lack of
practicing initiatives, lack of verification of what they saw during DO,
inconvenience in practicing settings, and poor ophthalmology exposure during
medical school. Therefore, we propose to develop a DO module consisting of
innovative demonstration videos, an application of a portable smartphone
ophthalmoscope (PSO) and a smartphone hand-held ophthalmoscopy simulator
(SOS) for self-evaluation and self-learning, and an interactive end-of-module
assessment scheme. Methods: Medical
students will undergo a DO workshop at the beginning of a 1-week
ophthalmology rotation. Students will be taught either by the original DO
(ODO group, which consists of a 1-hour lecture and hands-on DO practice
session) or the new DO module (NDO group, which consists of 3 innovative teaching videos, hands-on DO practice, use of PSO and SOS). All
students will also have their fundus photograph taken by a fundus camera.
During the rotation, students will practice DO on each other or patients.
Only the NDO group will be provided with the PSO (for cross-checking what
they saw with DO) and SOS (for practice and self-learning). At the end, they
will be assessed for their DO skill. This will be done by having students
dilate the pupil of one of their eyes (right or left) and examining another
student with the contralateral pupils dilated. The objective results will be
the tutor’s scores of the student’s DO skill, examination manner, completion
speed, and how accurately they could match the fundus photographs (taken
during the workshop). The subjective results will be the score of the
Anonymous Likert Scale Questionnaires (ALSQ) that the students will complete
at the end of the rotation. We will also provide the students with
opportunities for service-learning and working with external collaborators
(e.g., ORBIS, Jockey Club). The combination can achieve 1) interactive and
fun learning, 2) gaining of examinee’s experiences (student will understand
how the patients feel during eye examination), 3) enhancement of
student-teacher interaction, 4) motivating self-learning and students’
autonomy, and 5) application of knowledge and skill to serve society. The
effectiveness of the new module will be measured by comparing the subjective
and objective outcomes between the NDO and ODO groups. Potential: This
model could extend to other specialties in the CUHK MBChB curriculum, other universities’medical schools, and other courses in CUHK.
We aim to promote this concept and model to other university departments and
local educational institutions of all levels. |
|
72. |
Innovative Virtual Immersive Simulation to
Enhance Pharmacy Student’s Practical Lab Learning Experience: electronic
Practical Simulator (e-PS) platform |
Bachelor of Pharmacy is a four-year undergraduate program to train
students in various aspects of pharmacy, including dosage form sciences, to
ensure the safe usage of medication. In the Dosage Form Science courses,
pharmacy students integrate theoretical concepts covered in lectures and
tutorials, with physical laboratory practicals to
design, manufacture and evaluate pharmaceutical preparations. This holistic
approach is intended to equip students with hands-on skills and critical
thinking to identity and solve common instability issues which they may
encounter in their future pharmacy practice. The widespread use of smartphones, tablets, and other visual media
devices has a significant impact on the way students acquire knowledge, both
during and post the Covid-19 pandemic. The traditional black and white
paper-based lab manuals, that contain background concepts and detailed
experimental procedures in stepwise manner, may not be engaging enough for
the tech savvy students of today. Moreover, due to the comprehensive nature
of the pharmacy program, students’ timetable is quite packed, leaving them little
time to read through exhaustive written content. Since each practical lab has
various parts, students work in small groups and divide their lab-work.
Students tend to focus only on the part they are responsible for. This
approach limits individual students comprehensive learning of each lab. The proposed project aims to explore the use of micromodules and
virtual simulated immersive labs as a preparatory electronic Practical
Simulator (e-PS) platform, to complement physical practical labs. The e-PS
platform will assist students in gaining familiarity with the equipment,
procedures and expected outcomes, making their physical lab experience more
engaging, efficient and productive. These innovative visual learning
modalities would cater to students' preference for visual stimuli by
incorporating images, charts, virtual immersive simulations etc., into their
learning process. Moreover, the e-PS platform will be a useful virtual
learning preparatory tool that supports students in enhancing comprehension,
aiding in their information retention, and improving overall engagement. |
|
73. |
Development of Student-led Micro-modules in
Research and Leadership |
· Aim to develop a
series of student-led online micro-modules to enhance leadership training and
research skills for healthcare students. · Respond to the call
for innovative pedagogies at the programme level by adopting innovative
approaches to teaching development and language enhancement, improving the
learning environment for students. · Consist of two to
three micro-modules in each theme—leadership and research, resulting in a
total of six modules. · Complement the
existing 20 interactive leadership workshops embedded in the GPS curriculum. · Facilitate active
learning through the production of micro-modules, allowing participants to
absorb insights from experienced leaders and translate that knowledge into
actionable skills for future healthcare challenges. · Be integrated into the
CUHK Blackboard platform, providing broad access for students across various
healthcare disciplines. · Include quizzes and
feedback surveys to evaluate effectiveness and facilitate continuous
improvement. |
|
74. |
Enriching and Sustaining Quest2Learn: An
Integrated Smartphone-based Augmented Reality Platform for Gamification of
Laboratory Techniques |
· This project aims to
deepen virtual teaching and learning adoption by enriching a smartphone-based
augmented reality platform. · The platform
incorporates undergraduate science experiments and laboratory techniques.
Students will be able to gain practical hands-on laboratory skills in a
highly accessible virtual setting. · This project engages
students in teaching development. Learning modules are collaboratively
developed by students from CUHK and a partner university outside Hong Kong. · Six user-centered learning modules focusing on generic laboratory techniques and skills
will be produced. These modules will be used in
both pre-lab exercises and post-lab revisions for four laboratory courses.
Students’ learning are no longer limited to teaching
hours and laboratory venue. · Continuous improvement
will be achieved by regularly optimizing previous modules based on user
feedback. · The long-term goal of
this project is to develop a flexible virtual learning platform with a huge
database of learning modules and 3D models. Teaching units can design their
own virtual experiments under this platform for their teaching activities. |
|
75. |
Engaging Postgraduate Students in
Developing Virtual Teaching and Learning (VTL) Approaches to Facilitate Their
Learning of the Latest Scientific Discoveries and Most Advanced Experimental
Techniques |
Prof. Jiang
has recently been funded for
a RGC-CRF(E) project
entitled “The First
Integrated State-of- the-Art
Live Cell Imaging Platforms to Timely Promote Interdisciplinary and Advanced
Life Sciences Research in Hong
Kong and Beyond” in June 2022 (with a total fund of HK$20M for three years).
In addition, with the support of Prof. Jiang’s previously RGC-funded AoE/CRF-Equipment grants and CUHK matching fund, the
School of Life Sciences (SLS) at CUHK has recently established 3D TEM
(transmission electron microscopy) system, Cryo-EM/ET (Electron tomography) system and Cryo-FIB
(Focused Ion Beam) and Cryo-CLEM (Correlative Light-Electron Microscopy)
systems (with a total cost of HK$60M). With an arsenal of such advanced,
state-of-the-art equipment, the School of Life Sciences (SLS) is in a unique
position to offer one-of-a-kind learning experience to students in life
sciences. In this
project, Prof. Jiang and his team of professional researchers and teachers at
SLS will utilize the integrated research platforms to produce the following
deliverables to enhance teaching and learning: 1. To generate Discovery
Videos that introduce the scientific research process and our published
research discoveries derived from our integrated research platforms. 2. To generate Experiment
Videos on life sciences experiments that detail sample preparation and
experimental procedures utilizing the platforms. 3. To produce
micro-modules to enhance an existing mobile VR application in which students
could explore and interact with 3D structures of proteins and cellular
structures in a stimulating environment. 4. As these
high-quality deliverables are available online, this project is in line with
the Strategic Development Theme, “Deepening virtual teaching and learning
(VTL) adoption”, outlined in CUHK2025. In
addition, we will partner with postgraduate students from the research groups
in SLS to develop the micro-modules. Thus
we are also in line
with the Strategic Development Theme, “Engagement of students as partners in curriculum, teaching and teaching development”
and “Students taking ownership of their learning and stepping out of their
comfort zone”, outlined in CUHK2025. |
|
76. |
Supporting Statistics Research
Postgraduates to Teach Quantitative Data Analysis to Postgraduate Students
without Statistics Background – Phase II |
In the
2019-22 triennium, Phase
I of our project did the preparation work necessary for engaging statistics research postgraduates (Stat. RPgs) to teach
postgraduate students without
a statistics background (non- Stat. Pgs) by producing eight
micro-modules for a video training programme. The training covers
difficulties and anxiety in learning statistics for non-statistics background students, their learning needs, suggestions on planning workshops and suitable instructional techniques. Furthermore, an online course platform, "Statistical
methods for research students", was established, containing pre-workshop
videos, lecture materials and recordings. Two Stat. RPgs
successfully conducted two pilot statistics
workshops. Our team accumulated experience and learnt lessons from the students’ feedback on the pilot workshops. For Phase II of our project,
we will first enhance and expand on Phase I: over two years, 10 new Stat. RPgs will be recruited, trained then at least two
workshops each, preparing the related pre-workshop videos and materials
themselves. Secondly, our team will focus on enhancing workshop design and
planning to better support non-Stat. Pgs to learn
statistics more effectively under a blended approach. Thirdly, we will review
the effectiveness of the Stat.
RPg training programmes and make corresponding updates to the
micro-modules and training. |
|
77. |
Development of 3D Geoscience Virtual
Learning Platform and Outreach Schemes for the New Programme (EESC)
Integration and Community Engagement |
The
proposal from EESC consists of two major parts: (I)
Establishing a new and interactive 3D virtual educational platform, and (II)
sustainable engagement schemes in students' experiential learning.
(I) In the 2022-23
academic year, the Earth System Science (ESSC) is integrating with the
Environmental Science (ENSC) programme to form the Earth and Environmental
Sciences Programme (EESC). The new programme EESC emphasizes multidisciplinary approaches to understanding the
Earth. However, the current syllabus of most local
schools lacks an interdisciplinary pedagogy for preliminary study of the Earth systems from a scientific perspective. Many junior university students encounter difficulties
adapting to the new learning format, especially during the pandemic.
Implementing e-learning materials in ESSC courses
has evidently raised
students' interest and awareness of the scientific mechanisms generating
natural resources, geohazards, and environmental changes. This new way of
pedagogy assists students in achieving a promising learning outcome. To
support the new programme integration and deepen virtual teaching and learning
adaptation in EESC, our team thus proposes to establish the first local and interactive 3D geoscience virtual platform, including: (a)
production
of five virtual 3D models of local
geological features to understand the Earth's evolution; (b)
enhancing
Virtual Reality (VR) learning by creating
three local VR tours and three VR non-local tours for global geological,
geohazard, and environmental studies; (c)
generating a
Geochemical AR Education Kit, which includes new Augmented Reality (AR) gemstones
and modifying current AR mineral skeletons for a new EESC
course teaching natural resources and associated anthropogenic impacts; We believe
that this educational platform will fulfil geoscience course development in
EESC. Simultaneously, the platform will integrate and illustrate the
scientific concepts for interdisciplinary study, regardless of the COVID-19
impacts, and match the new global teaching norm. (II) Inadequate exposure to
Geoscience among students of local schools in Hong
Kong has resulted in a vast knowledge gap in the understanding of natural
resources, natural disasters, and environmental changes. There is also a lack
of public awareness of geoscientists' many roles in supporting sustainable
economic and ecological development in society. EESC is eager to promote a
coherent narrative of Geoscience as a STEM subject in Hong Kong. Our previous
experience and feedback from different parties provide blueprints to (a) enhance Geoscience Ambassador Training
Scheme (GATS) and (b) set up a Geoscience Outreach Scheme (GOS) to
sustain students' experiential learning and public education in Geoscience.
Our team proposes that the two schemes
be transformed into a credit-bearing Faculty-level course in the second
half of the project. The project transforms teaching and learning to an
integrated online and practical approach, encouraging cross- institutional
collaboration, engaging student participation, and experiential learning. Our
team expects that the project outcomes will contribute to the 17 United
Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) by demonstrating an innovative
geoscience pedagogy by formulating ideas for sustainable development in
industry, infrastructures, community, climate impacts, responsible
consumption, and partnerships for the goals (SDGs 9, 11, 12, 13, 15, 17). |
|
78. |
Elevating Undergraduate Chemistry: Data
Analysis with AI’s Machine Learning |
Machine
Learning (ML) has emerged as a powerful and widely utilized tool in
addressing a wide range of challenges within the field of chemistry.
Utilizing ML strategies, chemists can efficiently analyze vast, complex data
sets and make reliable predictions. Despite the increased prevalence of ML in
scientific research and development, fueled by the availability of modern ML
algorithms and high-performance computers, its incorporation into our
undergraduate chemistry curriculums is still lacking. This discrepancy leaves
our chemistry graduates unaware of the potential ML holds in solving complex
chemistry problems. This project
aims to bridge this gap by developing a series of laboratory activities that
introduce undergraduate students to the application of ML techniques in
chemistry, with a focus on tackling intricate spectroscopic analysis
problems. Those analyses usually involve identifying subtle spectral
differences that elude visual discrimination among a large
number of spectra. These activities will equip students with a
thorough understanding of several relevant aspects, including ML's basic
concepts, the necessary data pre-treatment before ML processes, the
implementation of ML in both non-coding and coding computing environments,
and the impact of different ML models on the outcomes of ML tasks. The
development and implementation of this series of teaching and learning
activities are designed to enhance AI literacy among our undergraduates,
preparing them to meet the demands of the current era. |
|
79. |
Development of Flashcard E-learning
Language Tool with The Aid of AI Chatbot |
Chemistry is
more than words and symbols on the textbooks as our life is always surrounded
by different kinds of chemicals. Even though Chemistry is so close to us,
students often find it as a difficult subject. Particularly during the
students’ first year of study, we notice that language barrier is always a
huge burden for students, who come from the Chinese Medium-of-instruction
(CMI) schools or from Gaokao of the Mainland China. It takes time for those
students to adopt the new learning and language environment in the
university. Sometimes it may cause them lots of frustrations and decrease
their learning interest and incentive. Our project will develop
flashcard-formatted gamification e-learning materials with the help of the AI
Chatbot. By employing this learning tool, we are able to
identify the strength and weakness of each student, provide extra support and
comments for them to overcome their weakness, including the language barrier,
enhance students’ learning engagement to the course and help students to
review their learning progress. This learning tool will be implemented in our
faculty package course CHEM1070A/B – Principles of Modern Chemistry, which
serves more than 350 students in every academic year. |
|
80. |
Virtual Project Supervisor for Supporting
Supervision of Statistics Projects |
The proposed project aims to develop a
chatbot using Large Language Models, such as ChatGPT. This chatbot will serve
as a virtual project supervisor, assisting in the monitoring and guidance of
student project progress throughout the course. Group projects have become common
learning activities and assessment methods in the undergraduate curriculum,
particularly in our department. We require all undergraduate students to
participate in project courses during their second, third, and final years.
These projects aim to enhance students' abilities to apply statistical
techniques practically, develop their communication skills, and encourage
teamwork. Currently, each project course instructor manages 10 or more groups
simultaneously, each with an average of six members. Actively monitoring all
group progress and providing timely support can be challenging for the
instructor. Without self-motivation and discipline, students may adopt
surface learning behaviors, rushing to complete
projects as deadlines approach. This can result in superficial project
deliverables due to insufficient research, inadequate analysis, and lack of
thoughtful interpretation. The proposed chatbot serves as a virtual
project supervisor, interacting with students via instant messaging apps like
WhatsApp in a project chat group. Students are encouraged to discuss their
projects in this group. The chatbot organizes these discussions, provides
summaries, and offers constructive feedback. It can also respond to basic
project-related questions, track progress, and assist students in achieving
project milestones. Throughout the project, all groups are required to
briefly and regularly report their progress, which includes an abstract,
timeline, brief literature review, study design, and summary of findings.
These updates should be submitted to the WhatsApp group via text messages.
These will be evaluated by both the instructor and AI (to be introduced in a
future update). These small and regular tasks are designed to promote regular
interaction with the chatbot and form part of the assessment criteria, aiding
in steady development of the final project report. In addition, the chatbot generates
progress summaries for each group and alerts instructors about any groups
that might need additional support. To evaluate the outcome, our project
team will gather feedback from students and project supervisors using surveys
and focus groups. This feedback will help us evaluate how the chatbot
improves teacher efficiency in group supervision, manages diverse groups,
affects students learning behavior, encourages
deeper learning, and enhances the quality of project deliverables. The
feedback will also guide us in refining and enhancing the chatbot for future
project courses. |
|
81. |
Data Mind Challenge: Fostering Global
Readiness through Ethical Data Analysis |
This project
proposes a 5-minute activity called the “Data Mind Challenge,” aimed at
enhancing students’ global readiness through data analytic skills that help
identify facts often misinterpreted by laypeople. Each challenge consists of
three components. First, a
video presents recent news, a globally relevant dataset, or a data analytic
problem. Created as a story, business scenario, or professional consultation,
the video mimics real-life situations students may face in practice,
academia, or the business world. The goal is to broaden students' horizons by
presenting problems of global interest. Second, one
data analytic skill or idea is introduced to help students extract meaning
from the problem. This skill addresses common statistical misuses, whether
intentional or unintentional, and provides guidance for the honest use of
statistical tools. The goal is to integrate high moral standards into data
literacy. Third, the
challenge concludes with a multiple-choice game that assesses students’
understanding of the problem. Upon completion, students receive a "Data
Mind Challenge" certificate as a downloadable social media post. The
goal is to encourage students to promote data science within their
communities. |
|
82. |
Exploring Virtual Reality (VR) as a Pedagogical
Tool in Supporting Collaborative and Experimental Learning |
In Hong
Kong, there is a persistent need across different disciplines to incorporate
new technological processes in teaching and learning programmes,
to address the increasing complexities of professional practice. In the post
Covid-19 paradigm, significant strain has been placed on academic programmes that are grounded in “signature pedagogies” such as Architecture to find more
effective avenues for the enhancement of ‘Design Thinking’ among students. In previous and ongoing teaching development initiatives by the PI,
the three themes
of SCAN, DESIGN, and BUILD have been shown to positively
contribute to student development. They can be framed through teaching and learning
experiences such as course development, technology adoption, discovery
learning and student aptitude for creative problem solving. As a
follow up to previous project ‘Virtual Reality (VR) for Integrated
3-Dimensional eLearning, Making and Immersive Communications’, this proposal
focuses more deeply on enhancing the DESIGN component within that
framework. It further breaks down the notion of ‘Design Thinking’ into
discrete categories: Abstraction,
Analysis, Simulation, Alteration, Communication, and System Building. The
proposal aims to develop and demonstrate how emerging technology can become
integral into the cultivation of design thinking, as part of an
evidence-based approach toward the development of an original design
position. Tools and novel technology – specifically
VR and integrated 3D/Virtual
drawing technology will be integrated into teaching and learning
practices to stimulate enhanced modes of visual, hands-on, and immersive
student learning experiences – all possible to be conducted in individual or
collaborative (group) modes. The expected outcomes from this will
be 1) an increased aptitude toward problem solving; 2) capacity to develop
subjective arguments based on clear criterion; 3) promotion of an original
design position; 4) increased sense of design confidence; 5) increased notion of design
identity (professional practice); 6) refined course
and programme planning for
instructors; 7) exposure to Virtual Reality and related technologies; 8)
virtual drawing hardware tools adapted for use within the virtual
environment. The teaching and learning processes within the programme will be evaluated as part of its ongoing development and as research into
the evolution of architectural education and design thinking through
technology adoption. |
|
83. |
CUHK CT-CITY – A new Metaverse Space for
Computational Thinking |
The goal
of this initiative is to create a novel metaverse city (CUHK CT-CITY) to
boost students’ computational thinking using computational social science
curricula. Alternative tools to learn computational abilities are necessary,
especially for social science and humanities majors, given the growing need
to process, analyze, and interpret big data. Computational thinking (CT) refers
to problem- solving skill
sets that apply concepts and reasoning derived from computer science.
Although CT is frequently associated with programming, there are few
non-programming approaches that can foster authentic and domain-specific knowledge. To address this
gap, this project leverages the potential of the metaverse—a place
for students to interact with
each other in a 3D virtual space—to evoke embodiment and immersion through authoring tools.
CUHK CT-CITY will
be made up of nine
3D virtual scenes
(eg. shop, park) in a city to support nine
digital stories, and will be integrated into an education-centric metaverse,
assisted by virtual agents, to teach CT. Students will use CT principles like abstraction and
sequencing in 20 minute lessons on social science
topics. Students can thus develop their topic knowledge, problem-solving
abilities, and capacity for independent thought in relation to big data. At
least three courses (e.g., SOCI3102, SOCI3229, and SOCI3238) will implement
the project. Partnering metaverse cities from
universities in Malaysia, Thailand, and Hong
Kong are also
expected to integrate. The innovative approach is
cross-disciplinary and is simple to apply to other fields, including medicine
and media literacy instruction. |
|
84. |
Enhancing Social Work Students' Clinical
Expertise Through Creative Bricks: The BUILD Model |
This project introduces an innovative approach to clinical social
work education through the integration of LEGO bricks, aiming to
revolutionize traditional teaching methodologies. By incorporating a
hands-on, interactive BUILD KIT and an Activity Guide into the curriculum,
this method fosters creativity, collaboration, and a crucial hand-brain
connection. This tactile learning experience enables students to actively
construct social work intervention models, thereby deepening their
understanding of clinical theories and practices in a collaborative
environment. The use of LEGO bricks as a tangible tool allows students to
visualize and internalize complex social work interventions across diverse
settings and clientele, facilitating both internal and external reflective
dialogues. This approach not only bridges the gap between theoretical
knowledge and practical application but also cultivates more effective,
empathetic practitioners equipped to handle the complexities of clinical
social work. By embedding the BUILD Model into the curriculum, this project
seeks to enhance student engagement, learning outcomes, and skill development
in a manner that aligns with the dynamic needs of the field. It invites the
academic community to support a transformative learning experience that
promises to prepare students for the multifaceted challenges of clinical
social work practice. |
|
85. |
From Immersive Learning to Real-life Experiential
Practice: Social Groupwork Education |
Social
groupwork is a professional intervention practice in social work that aims to
improve individuals’ social functioning through purposeful group experiences.
Formal social work education includes training in groupwork skills. However,
with the rapidly changing world, the needs of service recipients are
increasingly diverse and complex, and students face significant challenges in
practicing social groupwork in real-life situations. To enhance social work
students’ competence in practicing social groupwork, this project
incorporates computer simulation and virtual reality into the social work
curriculum design, and developing a 3-tier
educational plan. The plan includes integrating computer simulations and
virtual reality materials in the social groupwork curriculum, conducting
specialized workshops, and providing real-life group practice opportunities
to help students prepare and implement real-life services. This project
promotes academic, educational, and professional impacts in the university
and the community, such as developing a sustaining teaching and learning
culture in using technologies in social work education, enhancing students’
competence in using technologies in social work practice, and building a
supportive and resourceful learning network. |
|
86. |
Gimme Shelter |
The project “Gimme Shelter” addresses directly the alienation and
disaggregation of students that has been an acute problem since the
Coronavirus epidemic. The single biggest problem in the School of
Architecture is the motivation of students. Where “studio” —a method of
intensive, high contact teaching in small groups—has historically been the
beating heart of the school, we have found that morale in studio has been
weak in the past few years. The rate of student absenteeism has increased,
and the degree of horizontal learning has reduced to an extent that is
affecting graduate outcomes. Students display less interest in each other,
and each other’s work, than they should, and seem indifferent to each other’s
ideas. Many pedagogical projects have sought to ameliorate difficulties that
students have by offering more online content. This project asks students to
go emphatically offline. Participants will occupy an uninhabited island for two days—the
current preferred location is the island of Yim Tin Tsai, as its village
committee has already supported an architectural project, Wallace Chang’s ECO
Rotunda (see pdf associated with this email). The fundamental goal is
improvement of the espirit de corps
of Architecture and Urban Studies students. The second goal is directly
pedagogical: although sustainability is a major strategic goal of the
university, students report a fairly weak personal
relationship to the natural environment, and a correspondingly poor capacity
to tether sustainability goals to meaningful life experiences. Spending time
in structured exercises in natural environments should sharpen their
observational capacities and also their
environmental understanding. A third benefit of the project is the
improvement of solidarity amongst staff. |